The effect of gastric bypass on the pharmacokinetics of serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- PMID: 22407114
- PMCID: PMC3583374
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11050719
The effect of gastric bypass on the pharmacokinetics of serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Abstract
Objective: Morbidly obese patients frequently present with mood and anxiety disorders, which are often treated with serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs). Having observed that patients treated with SRIs frequently relapse after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, the authors sought to assess whether SRI bioavailability is reduced postoperatively.
Method: Twelve gastric bypass candidates treated with an SRI for primary mood or anxiety disorders were studied prospectively. Timed blood samples for SRI plasma levels were drawn for pharmacokinetic studies before surgery and 1, 6, and 12 months afterward. Maximum concentration, time to maximum concentration, and area under the concentration/time curve (AUC) were determined.
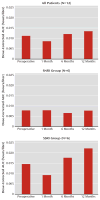
Results: In eight of the 12 patients, AUC values 1 month after surgery dropped to an average of 54% (SD=18) of preoperative levels (range=36%-80%); in six of these patients, AUC values returned to baseline levels (or greater) by 6 months. Four patients had an exacerbation of depressive symptoms, which resolved by 12 months in three of them. Three of the four patients had a reduced AUC level at 1 month and either gained weight or failed to lose weight between 6 and 12 months. Normalization of the AUC was associated with improvement in symptom scores.
Conclusions: Patients taking SRIs in this study were at risk for reduced drug bioavailability 1 month after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. The authors recommend close psychiatric monitoring after surgery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Weight Loss in Patients With Morbid Obesity: The SM-BOSS Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2018 Jan 16;319(3):255-265. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.20897. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 29340679 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Postoperative continuation of antidepressant therapy is associated with reduced short-term weight loss following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2019 Aug;404(5):621-631. doi: 10.1007/s00423-019-01784-z. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2019. PMID: 30969361
-
PBPK modeling of CYP3A and P-gp substrates to predict drug-drug interactions in patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2020 Oct;47(5):493-512. doi: 10.1007/s10928-020-09701-4. Epub 2020 Jul 24. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2020. PMID: 32710209
-
The effects of gastric bypass surgery on drug absorption and pharmacokinetics.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012 Dec;8(12):1505-19. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2012.722757. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22998066 Review.
-
Abdominal Pain After Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass for Morbid Obesity.Scand J Surg. 2018 Dec;107(4):277-284. doi: 10.1177/1457496918772360. Epub 2018 May 8. Scand J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29739280 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Pharmacokinetics of Drugs: a Review of Current Evidence.Curr Nutr Rep. 2023 Dec;12(4):695-708. doi: 10.1007/s13668-023-00498-5. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Curr Nutr Rep. 2023. PMID: 37857987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gestion des médicaments et changements pharmacocinétiques après la chirurgie bariatrique.Can Fam Physician. 2020 Jun;66(6):e171-e179. Can Fam Physician. 2020. PMID: 32532735 Free PMC article. Review. French.
-
Oral drug dosing following bariatric surgery: General concepts and specific dosing advice.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Dec;87(12):4560-4576. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14913. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33990981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery in Morbidly Obese Patients on Pharmacokinetics of (Acetyl)Salicylic Acid and Omeprazole: the ERY-PAO Study.Obes Surg. 2016 Sep;26(9):2051-2058. doi: 10.1007/s11695-016-2065-8. Obes Surg. 2016. PMID: 26797705 Clinical Trial.
-
Suicide attempts after bariatric surgery: comparison to a nonsurgical cohort of individuals with severe obesity.Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2023 Dec;19(12):1458-1466. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2023.08.013. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2023. PMID: 37758538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freedman DS. Obesity: United States, 1988–2008. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2011;60(suppl):73–77. - PubMed
-
- Onyike CU, Crum RM, Lee HB, Lyketsos CG, Eaton WW. Is obesity associated with major depression? results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Epidemiol. 2003;158:1139–1147. - PubMed
-
- Sarwer DB, Cohn NI, Gibbons LM, Magee L, Crerand CE, Raper SE, Rosato EF, Williams NN, Wadden TA. Psychiatric diagnoses and psychiatric treatment among bariatric surgery candidates. Obes Surg. 2004;14:1148–1156. - PubMed
-
- Alciati A, D’Ambrosio A, Foschi D, Corsi F, Mellado C, Angst J. Bipolar spectrum disorders in severely obese patients seeking surgical treatment. J Affect Disord. 2007;101:131–138. - PubMed
-
- Serretti A, Mandelli L. Antidepressants and body weight: a comprehensive review and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71:1259–1272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

