Proteasome inhibition can impair caspase-8 activation upon submaximal stimulation of apoptotic tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) signaling
- PMID: 22408249
- PMCID: PMC3340270
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.304378
Proteasome inhibition can impair caspase-8 activation upon submaximal stimulation of apoptotic tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) signaling
Abstract
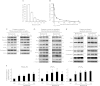
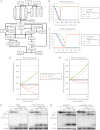
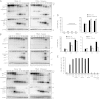
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) can induce extrinsic apoptosis, resulting in caspase-8 activation, but may also initiate transcription-dependent prosurvival signaling. Proteasome inhibitors were suggested to promote TRAIL signal transduction through the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) by modulating the relative abundance of core DISC components, thereby enhancing caspase-8 activation and apoptosis. To test this hypothesis, we quantified the changes in DISC protein levels as an early consequence of proteasome inhibition in HeLa cervical cancer cells and, based on these data, mathematically modeled the proapoptotic TRAIL signaling toward caspase-8 activation. Modeling results surprisingly suggested that caspase-8 activation might be delayed in presence of proteasome inhibitors, in particular at submaximal TRAIL doses. Subsequent FRET-based single cell time-lapse imaging at conditions where transcription dependent prosurvival signaling was blocked confirmed this hypothesis: caspase-8 activity was delayed by hours in the presence of proteasome inhibitors epoxomicin or bortezomib. Corresponding delays were detected for effector caspase processing and cell death. Contrary to current models, we therefore provide evidence that synergies between TRAIL and proteasome inhibitors do not result from changes in the levels of core DISC signaling proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proteasome inhibitors sensitize colon carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via enhanced release of Smac/DIABLO from the mitochondria.Pathol Oncol Res. 2006;12(3):133-42. doi: 10.1007/BF02893359. Epub 2006 Sep 23. Pathol Oncol Res. 2006. PMID: 16998592
-
Treating metastatic solid tumors with bortezomib and a tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor agonist antibody.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008 May 7;100(9):649-62. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djn113. Epub 2008 Apr 29. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008. PMID: 18445820 Free PMC article.
-
Bortezomib sensitizes human renal cell carcinomas to TRAIL apoptosis through increased activation of caspase-8 in the death-inducing signaling complex.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 May;8(5):729-38. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0022. Epub 2010 May 4. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20442297 Free PMC article.
-
Combining proteasome inhibition with TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (Apo2L/TRAIL) for cancer therapy.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006 Jan;55(1):76-84. doi: 10.1007/s00262-005-0676-3. Epub 2005 Oct 27. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006. PMID: 15864587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin as a proteasome inhibitor. Is there any clinical evidence?Life Sci. 2014 Oct 12;115(1-2):8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.08.024. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25219883 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of RIP and c-FLIP in preventing liver cancer cell apoptosis induced by TRAIL.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):6519-25. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261530 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering DED assembly mechanisms in FADD-procaspase-8-cFLIP complexes regulating apoptosis.Nat Commun. 2024 May 6;15(1):3791. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47990-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38710704 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating cell-to-cell variability and sensitivity to death ligands by co-drugging.Phys Biol. 2013 Jun;10(3):035002. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/10/3/035002. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Phys Biol. 2013. PMID: 23735516 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of apoptosis sensitivity through the interplay with autophagic and proteasomal degradation pathways.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jan 23;5(1):e1011. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.520. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24457955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling dynamics of cell-to-cell variability in TRAIL-induced apoptosis explains fractional killing and predicts reversible resistance.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Oct 23;10(10):e1003893. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003893. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 25340343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Konstantinova I. M., Tsimokha A. S., Mittenberg A. G. (2008) Role of proteasomes in cellular regulation. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 267, 59–124 - PubMed
-
- Brancolini C. (2008) Inhibitors of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and the cell death machinery: How many pathways are activated? Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 1, 24–37 - PubMed
-
- Concannon C. G., Koehler B. F., Reimertz C., Murphy B. M., Bonner C., Thurow N., Ward M. W., Villunger A., Strasser A., Kögel D., Prehn J. H. (2007) Apoptosis induced by proteasome inhibition in cancer cells: Predominant role of the p53/PUMA pathway. Oncogene 26, 1681–1692 - PubMed
-
- Pandey U. B., Nie Z., Batlevi Y., McCray B. A., Ritson G. P., Nedelsky N. B., Schwartz S. L., DiProspero N. A., Knight M. A., Schuldiner O., Padmanabhan R., Hild M., Berry D. L., Garza D., Hubbert C. C., Yao T. P., Baehrecke E. H., Taylor J. P. (2007) HDAC6 rescues neurodegeneration and provides an essential link between autophagy and the UPS. Nature 447, 859–863 - PubMed
-
- Pennarun B., Meijer A., de Vries E. G., Kleibeuker J. H., Kruyt F., de Jong S. (2010) Playing the DISC: Turning on TRAIL death receptor-mediated apoptosis in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1805, 123–140 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

