Composition, structure and functional properties of protein concentrates and isolates produced from walnut (Juglans regia L.)
- PMID: 22408408
- PMCID: PMC3291977
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms13021561
Composition, structure and functional properties of protein concentrates and isolates produced from walnut (Juglans regia L.)
Abstract
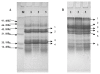
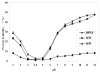
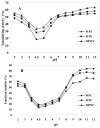
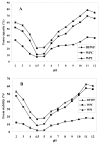
In this study, composition, structure and the functional properties of protein concentrate (WPC) and protein isolate (WPI) produced from defatted walnut flour (DFWF) were investigated. The results showed that the composition and structure of walnut protein concentrate (WPC) and walnut protein isolate (WPI) were significantly different. The molecular weight distribution of WPI was uniform and the protein composition of DFWF and WPC was complex with the protein aggregation. H(0) of WPC was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than those of DFWF and WPI, whilst WPI had a higher H(0) compared to DFWF. The secondary structure of WPI was similar to WPC. WPI showed big flaky plate like structures; whereas WPC appeared as a small flaky and more compact structure. The most functional properties of WPI were better than WPC. In comparing most functional properties of WPI and WPC with soybean protein concentrate and isolate, WPI and WPC showed higher fat absorption capacity (FAC). Emulsifying properties and foam properties of WPC and WPI in alkaline pH were comparable with that of soybean protein concentrate and isolate. Walnut protein concentrates and isolates can be considered as potential functional food ingredients.
Keywords: composition; functional properties; structure; walnut protein concentrate; walnut protein isolate.
Figures


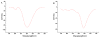
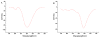

References
-
- Molina Ortiz S.E., Puppo M.C., Wagner J.R. Relationship between structural changes and functional properties of soy protein isolates—carrageenan systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2004;18:1045–1053.
-
- Yu J., Ahmedna M., Goktepe I. Peanut protein concentrate: Production and functional properties as affected by processing. Food Chem. 2007;103:121–129.
-
- Yoshie-Stark Y., Wada Y., Wäsche A. Chemical composition, functional properties, and bioactivities of rapeseed protein isolates. Food Chem. 2008;107:32–39.
-
- González-Pérez S., Vereijken J.M. Sunflower proteins: overview of their physicochemical, structural and functional properties. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2007;87:2173–2191.
-
- Sze-Tao K., Sathe S. Functional properties and in vitro digestibility of almond (Prunus dulcis L.) protein isolate. Food Chem. 2000;69:153–160.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

