A label-free electronic biosensor for detection of bone turnover markers
- PMID: 22408488
- PMCID: PMC3292091
- DOI: 10.3390/s91007957
A label-free electronic biosensor for detection of bone turnover markers
Abstract
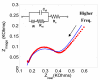
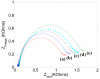
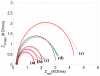
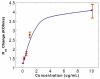
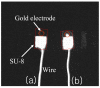
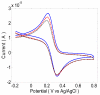
This paper describes the development of a biosensor based on label-free immunosensing for the detection of the C-terminal telopeptide bone turnover marker from type-1 collagen. A self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of dithiodipropionic acid was deposited on a gold electrode. Then streptavidin and biotinylated anti-human C-terminal telopeptide antibody were successively conjugated on the self-assembled monolayer. Electrochemical impedance measurements were made to characterize each step of the SAM/streptavidin/biotinylated antibody binding. Subsequently, electrochemical impedance was measured with different concentrations of C-teminal telopeptide. A detection limit of 50 ng/mL and a dynamic range up to 3 μg/mL were achieved. To our knowledge, this is the first attempt to develop a label-free immunosensor based on electrochemical impedance with DC bias for detection of bone-related degradation and rebuilding products. The electronic biosensor might eventually be used for quantitative point-of-care screening of bone health. It is hoped that analysis of bone turnover markers can indicate the beginning of bone diseases such as osteoarthritis and osteoporosis so that treatment might start early when it is most effective.
Keywords: bone turnover marker; electrochemical impedance; immunosensor; label-free.
Figures
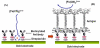


Similar articles
-
An Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on a Self-Assembled Monolayer Modified Electrode for Label-Free Detection of α-Synuclein.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jan 22;20(3):617. doi: 10.3390/s20030617. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31979160 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic Impedance Biosensor Chips Using Sensing Layers Based on DNA-Based Self-Assembled Monolayers for Label-Free Detection of Proteins.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 13;11(3):80. doi: 10.3390/bios11030080. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805676 Free PMC article.
-
Label-free electrochemical impedimetric immunosensor for sensitive detection of IgM rheumatoid factor in human serum.Biosens Bioelectron. 2019 Oct 15;143:111642. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.111642. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019. PMID: 31476598
-
Gold-coated carbon nanotube electrode arrays: Immunosensors for impedimetric detection of bone biomarkers.Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Mar 15;77:580-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.10.014. Epub 2015 Nov 14. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016. PMID: 26476598
-
A Portable Impedance Immunosensing System for Rapid Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Aug 28;17(9):1973. doi: 10.3390/s17091973. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28846643 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biosensors for Detection of Biochemical Markers Relevant to Osteoarthritis.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Jan 24;11(2):31. doi: 10.3390/bios11020031. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33561091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Situ Sensor Advancements for Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016 Dec;14(6):386-395. doi: 10.1007/s11914-016-0339-7. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016. PMID: 27815807 Review.
-
Emerging Technologies and Platforms for the Immunodetection of Multiple Biochemical Markers in Osteoarthritis Research and Therapy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Oct 21;7:572977. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.572977. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33195320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic chip immunoassay based on rolling circle amplification and G-quadruplex/Thioflavin T for multiplex detection of CTX I.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Feb 28;191(3):165. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06240-4. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38416241
-
Rapid electrochemical immunodetection of SARS-CoV-2 using a pseudo-typed vesicular stomatitis virus model.Talanta. 2022 Mar 1;239:123147. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123147. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Talanta. 2022. PMID: 34920254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seeman E., Delmas P.D. Bone quality-the material and structural basis of bone strength and fragility. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:2250–2261. - PubMed
-
- Ryouji M., Itsuo Y., Masahiko T., Yasuyo H., Itsuaki Y., Rikushi M. Comparison of various biochemical measurements with bone mineral densitometry and quantitative ultrasound for the assessment of vertebral fracture. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2000;18:158–168. - PubMed
-
- Watts N.B. Clinical utility of biochemical markers of bone remodeling. Clin. Chem. 1999;45:1359–1368. - PubMed
-
- Bone Health and Osteoporosis Center; Southington, CT, USA: 2008. Review and search engine for osteoporosis. Available at: http://www.ucosteoporosis.com/ (accessed 31 May 2008)
-
- Burgeson R.E. Serum cross Laps one step ELISA: first application of monoclonal antibodies for measurement in serum of bone-related degradation products from C-terminal telopeptides of type I collagen. Annu. Rev. Cell. Biol. 1998;4:552–577. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

