Metabolomic profiles of myocardial ischemia under treatment with salvianolic acid B
- PMID: 22409910
- PMCID: PMC3317850
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-8546-7-6
Metabolomic profiles of myocardial ischemia under treatment with salvianolic acid B
Abstract
Background: Radix Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) has been used as a principal herb in treating cardiovascular diseases in Chinese medicine. Salvianolic acid B (SA-B), a water-soluble active component of Danshen, was found to have anti-myocardial ischemia (anti-MI) effect. This study aims to investigate mechanisms of SA-B on MI.
Methods: Five conventional Western medicines (isosorbide dinitrate, verapamil, propranolol, captopril and trimethazine) with different mechanisms for treating cardiovascular diseases were selected as positive references to compare with SA-B in changing of the metabolomic profiles in MI rats under treatment. Potential mechanisms of SA-B were further investigated in H9C2 cell line.
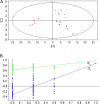
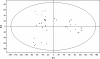
Results: The metabolomic profiles between SA-B- and propranolol-treated MI rats were similar, since there was a big overlap between the two groups in the PLS-DA score plot. Finally, it was demonstrated that SA-B exhibited a protective effect on MI mainly by decreasing the concentration of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and Ca2+ and inhibiting protein kinase A (PKA).
Conclusion: SA-B and propanolol exhibited similar metabolomic profiles, indicating that the two drugs might have a similar mechanism.
Figures
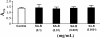
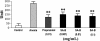
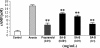
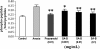
References
-
- World Health Organization. Department of Health Statistics and Informatics in the Information, Evidence and Research Cluster. The global burden of disease 2004 update. Geneva: WHO; 2004.
-
- Chakraborti S, Das S, Kar P, Ghosh B, Samanta K, Kolley S, Ghosh S, Roy S, Chakraborti T. Calcium signaling phenomena in heart diseases: a perspective. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007;29:l–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

