Gold nanoparticles as high-resolution X-ray imaging contrast agents for the analysis of tumor-related micro-vasculature
- PMID: 22409971
- PMCID: PMC3316138
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3155-10-10
Gold nanoparticles as high-resolution X-ray imaging contrast agents for the analysis of tumor-related micro-vasculature
Abstract
Background: Angiogenesis is widely investigated in conjunction with cancer development, in particular because of the possibility of early stage detection and of new therapeutic strategies. However, such studies are negatively affected by the limitations of imaging techniques in the detection of microscopic blood vessels (diameter 3-5 μm) grown under angiogenic stress. We report that synchrotron-based X-ray imaging techniques with very high spatial resolution can overcome this obstacle, provided that suitable contrast agents are used.
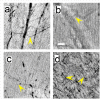
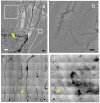
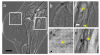
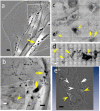
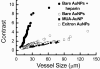
Results: We tested different contrast agents based on gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for the detection of cancer-related angiogenesis by synchrotron microradiology, microtomography and high resolution X-ray microscopy. Among them only bare-AuNPs in conjunction with heparin injection provided sufficient contrast to allow in vivo detection of small capillary species (the smallest measured lumen diameters were 3-5 μm). The detected vessel density was 3-7 times higher than with other nanoparticles. We also found that bare-AuNPs with heparin allows detecting symptoms of local extravascular nanoparticle diffusion in tumor areas where capillary leakage appeared.
Conclusions: Although high-Z AuNPs are natural candidates as radiology contrast agents, their success is not guaranteed, in particular when targeting very small blood vessels in tumor-related angiography. We found that AuNPs injected with heparin produced the contrast level needed to reveal--for the first time by X-ray imaging--tumor microvessels with 3-5 μm diameter as well as extravascular diffusion due to basal membrane defenestration. These results open the interesting possibility of functional imaging of the tumor microvasculature, of its development and organization, as well as of the effects of anti-angiogenic drugs.
Figures


References
-
- Meuli R, Hwu Y, Je JH, Margaritondo G. Synchrotron radiation in radiology--part II: radiology techniques based on synchrotron sources. Eur Radiol. 2004;14:1550–1560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

