SIRT1 deacetylase promotes acquisition of genetic mutations for drug resistance in CML cells
- PMID: 22410779
- PMCID: PMC3376246
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.83
SIRT1 deacetylase promotes acquisition of genetic mutations for drug resistance in CML cells
Abstract
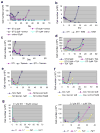
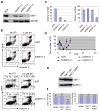
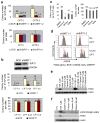
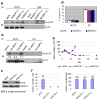
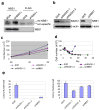
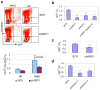
BCR-ABL transforms bone marrow progenitor cells and promotes genome instability, leading to development of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). The tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib effectively treats CML, but acquired resistance can develop because of BCR-ABL mutations. Mechanisms for acquisition of BCR-ABL mutations are not fully understood. Using a novel culture model of CML acquired resistance, we show that inhibition of SIRT1 deacetylase by small molecule inhibitors or gene knockdown blocks acquisition of BCR-ABL mutations and relapse of CML cells on tyrosine kinase inhibitors. SIRT1 knockdown also suppresses de novo genetic mutations of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase gene in CML and non-CML cells upon treatment with DNA damaging agent camptothecin. Although SIRT1 can enhance cellular DNA damage response, it alters functions of DNA repair machineries in CML cells and stimulates activity of error-prone DNA damage repair, in association with acquisition of genetic mutations. These results reveal a previously unrecognized role of SIRT1 for promoting mutation acquisition in cancer, and have implication for targeting SIRT1 to overcome CML drug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosure: Parts of this manuscript were used for a patent application filed by City of Hope.
Figures
References
-
- Melo JV, Barnes DJ. Chronic myeloid leukaemia as a model of disease evolution in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:441–453. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–2417. - PubMed
-
- Deininger MW, Druker BJ. Specific targeted therapy of chronic myelogenous leukemia with imatinib. Pharmacol Rev. 2003;55:401–423. - PubMed
-
- Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN, et al. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science. 2001;293:876–880. - PubMed
-
- Shah NP, Nicoll JM, Nagar B, Gorre ME, Paquette RL, Kuriyan J, et al. Multiple BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations confer polyclonal resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571) in chronic phase and blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:117–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

