Governing epidermal homeostasis by coupling cell-cell adhesion to integrin and growth factor signaling, proliferation, and apoptosis
- PMID: 22411810
- PMCID: PMC3324018
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1202120109
Governing epidermal homeostasis by coupling cell-cell adhesion to integrin and growth factor signaling, proliferation, and apoptosis
Abstract
Cadherin/catenin-based adhesions coordinate cellular growth, survival, migration, and differentiation within a tissue by mechanically anchoring cells to their neighbors. They also intersect with diverse signaling pathways in development and cancer. Although the adhesive functions of adherens junction proteins are well characterized, their contribution to other signaling pathways is less well understood. Here, we show that ablation of α-catenin in the epidermis selectively induces apoptosis in suprabasal differentiating keratinocytes while sparing basal cell progenitors. This protection from death is coupled to elevated focal adhesion signaling, faster migration, and an altered distribution of growth factor receptors. We show that simultaneous depletion of α-catenin and focal adhesion kinase or p21-activated kinase eliminates basal cell protection as well as the elevated migration and proliferation of cells. The increased dependency of cells upon matrix interactions for their survival when cell-cell adhesions are destabilized has important implications for cancer progression and metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


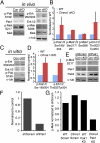

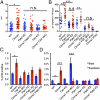
References
-
- Halbleib JM, Nelson WJ. Cadherins in development: Cell adhesion, sorting, and tissue morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 2006;20:3199–3214. - PubMed
-
- Vasioukhin V, Bauer C, Degenstein L, Wise B, Fuchs E. Hyperproliferation and defects in epithelial polarity upon conditional ablation of alpha-catenin in skin. Cell. 2001;104:605–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

