Tetrodotoxin (TTX) as a therapeutic agent for pain
- PMID: 22412801
- PMCID: PMC3296997
- DOI: 10.3390/md10020281
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) as a therapeutic agent for pain
Abstract
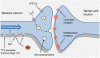
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin that blocks voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs). VGSCs play a critical role in neuronal function under both physiological and pathological conditions. TTX has been extensively used to functionally characterize VGSCs, which can be classified as TTX-sensitive or TTX-resistant channels according to their sensitivity to this toxin. Alterations in the expression and/or function of some specific TTX-sensitive VGSCs have been implicated in a number of chronic pain conditions. The administration of TTX at doses below those that interfere with the generation and conduction of action potentials in normal (non-injured) nerves has been used in humans and experimental animals under different pain conditions. These data indicate a role for TTX as a potential therapeutic agent for pain. This review focuses on the preclinical and clinical evidence supporting a potential analgesic role for TTX. In addition, the contribution of specific TTX-sensitive VGSCs to pain is reviewed.
Keywords: TTX; TTX-sensitive voltage-gated sodium channels; neuropathic pain; pain; tetrodotoxin.
Figures

References
-
- Dib-Hajj S.D., Cummins T.R., Black J.A., Waxman S.G. Sodium channels in normal and pathological pain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2010;33:325–347. - PubMed
-
- Catterall W.A. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: The structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 2000;26:13–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

