Evolution of JAK-STAT pathway components: mechanisms and role in immune system development
- PMID: 22412924
- PMCID: PMC3296744
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032777
Evolution of JAK-STAT pathway components: mechanisms and role in immune system development
Abstract
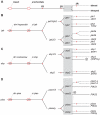
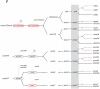
Background: Lying downstream of a myriad of cytokine receptors, the Janus kinase (JAK)-Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway is pivotal for the development and function of the immune system, with additional important roles in other biological systems. To gain further insight into immune system evolution, we have performed a comprehensive bioinformatic analysis of the JAK-STAT pathway components, including the key negative regulators of this pathway, the SH2-domain containing tyrosine phosphatase (SHP), Protein inhibitors against Stats (PIAS), and Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins across a diverse range of organisms.
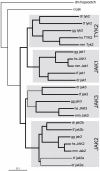
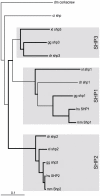
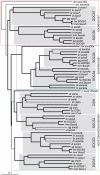
Results: Our analysis has demonstrated significant expansion of JAK-STAT pathway components co-incident with the emergence of adaptive immunity, with whole genome duplication being the principal mechanism for generating this additional diversity. In contrast, expansion of upstream cytokine receptors appears to be a pivotal driver for the differential diversification of specific pathway components.
Conclusion: Diversification of JAK-STAT pathway components during early vertebrate development occurred concurrently with a major expansion of upstream cytokine receptors and two rounds of whole genome duplications. This produced an intricate cell-cell communication system that has made a significant contribution to the evolution of the immune system, particularly the emergence of adaptive immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







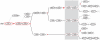
References
-
- Ozaki K, Leonard WJ. Cytokine and cytokine receptor pleiotropy and redundancy. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:29355–29358. - PubMed
-
- Voss SD, Hong R, Sondel PM. Severe combined immunodeficiency, interleukin-2 (IL-2), and the IL-2 receptor: experiments of nature continue to point the way. Blood. 1994;83:626–635. - PubMed
-
- Kotenko SV, Gallagher G, Baurin VV, Lewis-Antes A, Shen M, et al. IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Liongue C, Wright C, Russell AP, Ward AC. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor: stimulating granulopoiesis and much more. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;41:2372–2375. - PubMed
-
- Seubert N, Royer Y, Staerk J, Kubatzky KF, Moucadel V, et al. Active and inactive orientations of the transmembrane and cytosolic domains of the erythropoietin receptor dimer. Mol Cell. 2003;12:1239–1250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

