Peripheral arterial and venous response to tilt test after a 60-day bedrest with and without countermeasures (ES-IBREP)
- PMID: 22412933
- PMCID: PMC3296756
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032854
Peripheral arterial and venous response to tilt test after a 60-day bedrest with and without countermeasures (ES-IBREP)
Abstract
We quantified the impact of 60-day head-down bed rest (HDBR) with countermeasures on arterial and venous response to tilt.
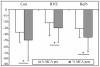
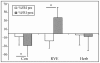
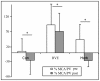
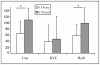
Methods: Twenty-one males: 7 control (Con), 7 resistive vibration exercise (RVE) and 7 Chinese herb (Herb) were assessed. Subjects were identified as finisher (F) or non-finishers (NF) at the post-HDBR 20-min tilt test. The cerebral (MCA), femoral (FEM) arterial flow velocity and leg vascular resistance (FRI), the portal vein section (PV), the flow redistribution ratios (MCA/FEM; MCA/PV), the tibial (Tib), gastrocnemius (Gast), and saphenous (Saph) vein sections were measured by echography and Doppler ultrasonography. Arterial and venous parameters were measured at 3-min pre-tilt in the supine position, and at 1 min before the end of the tilt.
Results: At post-HDBR tilt, MCA decreased more compared with pre-HDBR tilt in the Con, RVE, and Herb groups, the MCA/FEM tended to decrease in the Con and Herb groups (not significant) but remained stable in the RVE gr. FRI dropped in the Con gr, but remained stable in the Herb gr and increased in the RVE gr. PV decreased less in the Con and Herb groups but remained unchanged in the RVE gr. MCA/PV decreased in the Con and Herb groups, but increased to a similar extent in the RVE gr. Gast section significantly increased more in the Con gr only, whereas Tib section increased more in the Con and Herb groups but not in the RVE gr. The percent change in Saph section was similar at pre- and post-HDBR tilt.
Conclusion: In the Con gr, vasoconstriction was reduced in leg and splanchnic areas. RVE and Herb contributed to prevent the loss of vasoconstriction in both areas, but the effect of RVE was higher. RVE and Herb contributed to limit Gast distension whereas only RVE had a protective effect on the Tib.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Temporal artery flow response during the last minute of a head up tilt test, in relation with orthostatic intolerance after a 60 day head-down bedrest.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e22963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022963. Epub 2011 Oct 26. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22073117 Free PMC article.
-
WISE-2005: tibial and gastrocnemius vein and calf tissue response to LBNP after a 60-day bed rest with and without countermeasures.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008 Apr;104(4):938-43. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01021.2007. Epub 2008 Jan 17. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008. PMID: 18202168
-
Insufficient flow reduction during LBNP in both splanchnic and lower limb areas is associated with orthostatic intolerance after bedrest.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Nov;295(5):H1846-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.509.2008. Epub 2008 Aug 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18757480 Clinical Trial.
-
Aortic, cerebral and lower limb arterial and venous response to orthostatic stress after a 60-day bedrest.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012 Jan;112(1):277-84. doi: 10.1007/s00421-011-1935-y. Epub 2011 May 4. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21541764
-
Arterial and venous response to Tilt with LBNP test after a 60 day HDT bedrest (WISE study).J Gravit Physiol. 2007 Jul;14(1):P47-8. J Gravit Physiol. 2007. PMID: 18372693 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Effect of Chinese herbal medicine on vascular functions during 60-day head-down bed rest.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2015 Sep;115(9):1975-83. doi: 10.1007/s00421-015-3176-y. Epub 2015 May 9. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25957107 Clinical Trial.
-
Vascular and Microvascular Dysfunction Induced by Microgravity and Its Analogs in Humans: Mechanisms and Countermeasures.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 20;11:952. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00952. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32973543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Space physiology VI: exercise, artificial gravity, and countermeasure development for prolonged space flight.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013 Sep;113(9):2183-92. doi: 10.1007/s00421-012-2523-5. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23079865 Review.
-
Bone protection effects of a novel Chinese herbal formula, taikong yangxin prescription, in hindlimb unloaded rats against bone deterioration.Chin J Integr Med. 2015 Oct;21(10):759-64. doi: 10.1007/s11655-015-2310-3. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Chin J Integr Med. 2015. PMID: 26525547
References
-
- Buckey JC, Jr, Lane LD, Levine BD, Watenpaugh DE, Wright SJ, et al. Orthostatic intolerance after spaceflight. J Appl Physiol. 1996;81(1):7–18. - PubMed
-
- Arbeille P, Besnard S, Kerbeci P, Mohty D. Portal vein cross-sectional area and flow and orthostatic tolerance: a 90-day bed rest study. J Appl Physiol. 2005;99:1853–7. - PubMed
-
- Arbeille P, Kerbeci P, Mattar L, Shoemaker JK, Hughson RL. Insufficient flow reduction during LBNP in both splanchnic & lower limb areas is associated with orthostatic intolerance after bedrest. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008;295(5):1846–54. - PubMed
-
- Arbeille P, Kerbeci P, Mattar L, Shoemaker JK, Hughson RL. Wise-2005: Tibial and gastrocnemius vein, and calf tissue response to LBNP after a 60 d bedrest with & without countermeasure. J Appl Physiol. 2008;104(4):938–43. - PubMed
-
- Herault S, Tobal N, Normand H, Roumy J, Denise P, et al. Effect of head flexion on the control of peripheral blood flow in microgravity and in 1 g. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2002;87(3):296–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

