Oxidative stress induced interleukin-32 mRNA expression in human bronchial epithelial cells
- PMID: 22413812
- PMCID: PMC3361495
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-19
Oxidative stress induced interleukin-32 mRNA expression in human bronchial epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by airflow obstruction and persistent inflammation in the airways and lung parenchyma. Oxidative stress contributes to the pathogenesis of COPD. Interleukin (IL)-32 expression has been reported to increase in the lung tissue of patients with COPD. Here, we show that IFNγ upregulated IL-32 expression and that oxidative stress augmented IFNγ-induced-IL-32 expression in airway epithelial cells. We further investigated transcriptional regulation responsible for IFNγ induced IL-32 expression in human airway epithelial cells.
Methods: Human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells were stimulated with H2O2 and IFNγ, and IL-32 expression was evaluated. The cell viability was confirmed by MTT assay. The intracellular signaling pathways regulating IL-32 expression were investigated by examining the regulatory effects of MAPK inhibitors and JAK inhibitor after treatment with H2O2 and IFNγ, and by using a ChIP assay to identify transcription factors (i.e. c-Jun, CREB) binding to the IL-32 promoter. Promoter activity assays were conducted after mutations were introduced into binding sites of c-Jun and CREB in the IL-32 promoter. IL-32 expression was also examined in HBE cells in which the expression of either c-Jun or CREB was knocked out by siRNA of indicated transcription factors.
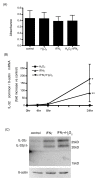
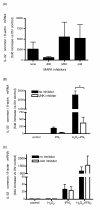
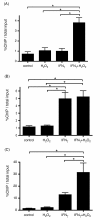
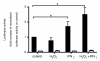
Results: There were no significant differences of cell viability among groups. After stimulation with H2O2 or IFNγ for 48 hours, IL-32 expression in HBE cells was increased by IFNγ and synergistically upregulated by the addition of H2O2. The H2O2 augmented IFNγ induced IL-32 mRNA expression was suppressed by a JNK inhibitor, but not by MEK inhibitor, p38 inhibitor, and JAK inhibitor I. Significant binding of c-Jun and CREB to the IL-32 promoter was observed in the IFNγ + H2O2 stimulated HBE cells. Introducing mutations into the c-Jun/CREB binding sites in the IL-32 promoter prominently suppressed its transcriptional activity. Further, knocking down CREB expression by siRNA resulted in significant suppression of IL-32 induction by IFNγ and H2O2 in HBE cells.
Conclusion: IL-32 expression in airway epithelium may be augmented by inflammation and oxidative stress, which may occur in COPD acute exacerbation. c-Jun and CREB are key transcriptional factors in IFNγ and H2O2 induced IL-32 expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 up-regulate monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in human bronchial epithelial cells: involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and Janus kinase-2 but not c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1/2 signalling pathways.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Jul;145(1):162-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03085.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16792687 Free PMC article.
-
The IL-17F signaling pathway is involved in the induction of IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10 in bronchial epithelial cells.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007 Jun;119(6):1408-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.02.036. Epub 2007 Apr 5. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17418381
-
Oxidative stress enhances the expression of IL-33 in human airway epithelial cells.Respir Res. 2018 Mar 27;19(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0752-9. Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 29587772 Free PMC article.
-
15-Deoxy-prostaglandin J2 anti-inflammation in a rat model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and human bronchial epithelial cells via Nrf2 activation.Genet Mol Res. 2015 Oct 30;14(4):14037-42. doi: 10.4238/2015.October.29.22. Genet Mol Res. 2015. PMID: 26535717
-
TGFβ1 induces IL-6 and inhibits IL-8 release in human bronchial epithelial cells: the role of Smad2/3.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Nov;225(3):846-54. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22295. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20607798
Cited by
-
Role of interleukin-32 in chronic rhinosinusitis.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Feb;13(1):13-8. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e32835b35d5. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23242112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse Expression of IL-32 in Diffuse and Intestinal Types of Gastric Cancer.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018 Oct 4;2018:6578273. doi: 10.1155/2018/6578273. eCollection 2018. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30402092 Free PMC article.
-
A Critical Overview of Interleukin 32 in Leishmaniases.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 3;13:849340. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.849340. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation between serum IL-32 concentration and clinical parameters of stable COPD: a retrospective clinical analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 21;10(1):12092. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69000-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32694699 Free PMC article.
-
A panoramic spectrum of complex interplay between the immune system and IL-32 during pathogenesis of various systemic infections and inflammation.Eur J Med Res. 2015 Jan 28;20(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40001-015-0083-y. Eur J Med Res. 2015. PMID: 25626592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

