A unique role of cohesin-SA1 in gene regulation and development
- PMID: 22415368
- PMCID: PMC3343463
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.60
A unique role of cohesin-SA1 in gene regulation and development
Abstract
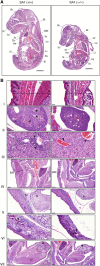
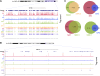
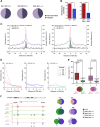
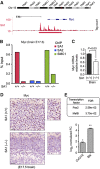
Vertebrates have two cohesin complexes that consist of Smc1, Smc3, Rad21/Scc1 and either SA1 or SA2, but their functional specificity is unclear. Mouse embryos lacking SA1 show developmental delay and die before birth. Comparison of the genome-wide distribution of cohesin in wild-type and SA1-null cells reveals that SA1 is largely responsible for cohesin accumulation at promoters and at sites bound by the insulator protein CTCF. As a consequence, ablation of SA1 alters transcription of genes involved in biological processes related to Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS), a genetic disorder linked to dysfunction of cohesin. We show that the presence of cohesin-SA1 at the promoter of myc and of protocadherin genes positively regulates their expression, a task that cannot be assumed by cohesin-SA2. Lack of SA1 also alters cohesin-binding pattern along some gene clusters and leads to dysregulation of genes within. We hypothesize that impaired cohesin-SA1 function in gene expression underlies the molecular aetiology of CdLS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

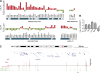
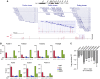

Comment in
-
The many functions of cohesin--different rings to rule them all?EMBO J. 2012 May 2;31(9):2061-3. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.90. Epub 2012 Apr 10. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22491011 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castronovo P, Gervasini C, Cereda A, Masciadri M, Milani D, Russo S, Selicorni A, Larizza L (2009) Premature chromatid separation is not a useful diagnostic marker for Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Chromosome Res 17: 763–771 - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Xu H, Yuan P, Fang F, Huss M, Vega VB, Wong E, Orlov YL, Zhang W, Jiang J, Loh YH, Yeo HC, Yeo ZX, Narang V, Govindarajan KR, Leong B, Shahab A, Ruan Y, Bourque G, Sung WK et al. (2008) Integration of external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network in embryonic stem cells. Cell 133: 1106–1117 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

