Diagnostic accuracy of mediastinal width measurement on posteroanterior and anteroposterior chest radiographs in the depiction of acute nontraumatic thoracic aortic dissection
- PMID: 22415593
- PMCID: PMC3396328
- DOI: 10.1007/s10140-012-1034-3
Diagnostic accuracy of mediastinal width measurement on posteroanterior and anteroposterior chest radiographs in the depiction of acute nontraumatic thoracic aortic dissection
Abstract
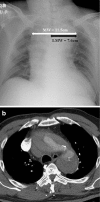
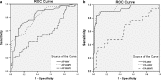
We aimed to explore the diagnostic accuracy of various mediastinal measurements in determining acute nontraumatic thoracic aortic dissection with respect to posteroanterior (PA) and anteroposterior (AP) chest radiographs, which had received little attention so far. We retrospectively reviewed 100 patients (50 PA and 50 AP chest radiographs) with confirmed acute thoracic aortic dissection and 120 patients (60 PA and 60 AP chest radiographs) with confirmed normal aorta. Those who had prior history of trauma or aortic disease were excluded. The maximal mediastinal width (MW) and maximal left mediastinal width (LMW) were measured by two independent radiologists and the mediastinal width ratio (MWR) was calculated. Statistical analysis was then performed with independent sample t test. PA projection was significantly more accurate than AP projection, achieving higher sensitivity and specificity. LMW and MW were the most powerful parameters on PA and AP chest radiographs, respectively. The optimal cutoff levels were LMW = 4.95 cm (sensitivity, 90 %; specificity, 90 %) and MW = 7.45 cm (sensitivity, 90 %; specificity, 88.3 %) for PA projection and LMW = 5.45 cm (sensitivity, 76 %; specificity, 65 %) and MW = 8.65 cm (sensitivity, 72 %; specificity, 80 %) for AP projection. MWR was found less useful and less reliable. The use of LMW alone in PA film would allow more accurate prediction of aortic dissection. PA chest radiograph has a higher diagnostic accuracy when compared with AP chest radiograph, with negative PA chest radiograph showing less probability for aortic dissection. Lower threshold for proceeding to computed tomography aortogram is recommended however, especially in the elderly and patients with widened mediastinum on AP chest radiograph.
Figures


References
-
- Thoongsuwan N, Stern EJ. Chest CT scanning for clinical suspected thoracic aortic dissection: beware the alternate diagnosis. Emerg Radiol. 2002;9:257–261. - PubMed
-
- Peters DR, Gamsu G. Displacement of the right paraspinous interface: a radiographic sign of acute traumatic rupture of the thoracic aorta. Radiology. 1980;134:599–603. - PubMed
-
- Simeone JF, Deren MM, Cagle F. The value of the left apical cap in the diagnosis of aortic rupture: a prospective and retrospective study. Radiology. 1981;139:35–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

