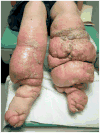
Elephantiatic dermopathy
- PMID: 22417118
- PMCID: PMC4334560
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05275.x
Elephantiatic dermopathy
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None.
Figures

References
-
- Schwartz KM, Fatourechi V, Ahmed DD, Pond GR. Dermopathy of Graves' disease (pretibial myxedema): longterm outcome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:438–446. - PubMed
-
- Fatourechi V, Bartley GB, Eghbali-Fatourechi GZ, et al. Graves' dermopathy and acropachy are markers of severe Graves' ophthalmopathy. Thyroid. 2003;13:1141–1144. - PubMed
-
- Rongioletti F, Donati P, Amantea A, et al. Obesity-associated lymphedematous mucinosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:1089–1094. - PubMed
-
- Konrad K, Brenner W, Pehamberger H. Ultrastructural and immunological findings in Graves' disease with pretibial myxedema. J Cutan Pathol. 1980;7:99–108. - PubMed
-
- Kobayasi T, Danielsen L, Asboe-Hansen G. Ultrastructure of localized myxedema. Acta Derm Venereol. 1976;56:173–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

