Mouse model of touch-evoked itch (alloknesis)
- PMID: 22418875
- PMCID: PMC3375351
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2012.52
Mouse model of touch-evoked itch (alloknesis)
Abstract
Lightly touching normal skin near a site of itch can elicit itch sensation, a phenomenon known as alloknesis. To investigate the neural mechanisms of alloknesis, we have developed an animal model. Low-threshold mechanical stimulation of the skin normally does not elicit any response in naive C57/BL6 mice. Following acute intradermal (i.d.) injection of histamine in the rostral back, mechanical stimulation 7 mm from the injection site elicited discrete hindlimb scratch bouts directed toward the stimulus. This began at 10 minutes and peaked 20-40 minutes post histamine injection, declining over the next hour. Histamine itself elicited bouts of scratching not associated with the mechanical stimulus, which ceased after 30 minutes. Histamine- and touch-evoked scratching was inhibited by the μ-opiate antagonist naltrexone. Touch-evoked scratching was observed following i.d. 5-HT (5-hydroxytryptamine), a protease-activated receptor (PAR)-4 agonist, and an MrgprC11 agonist BAM8-22, but not chloroquine or a PAR-2 agonist. The histamine H1 receptor antagonist terfenadine prevented scratching and alloknesis evoked by histamine, but not 5-HT, a PAR-4 agonist or an MrgprC11 agonist. In mice with experimental dry skin, there was a time-dependent increase in spontaneous and touch-evoked scratching. This animal model appears to be useful to investigate neural mechanisms of itch and alloknesis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: none.
Figures
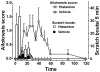
 ) or vehicle (
) or vehicle (
 ). Error bars are S.E.M. (n = 6/ group). Following intradermal injection of histamine (271 nmol/10 μl; open bars and
). Error bars are S.E.M. (n = 6/ group). Following intradermal injection of histamine (271 nmol/10 μl; open bars and
 ) or saline (vehicle; filled bars and
) or saline (vehicle; filled bars and
 ) in the nape of the neck, the mouse was placed into the recording arena and videotaped for 30 min. At 5-min intervals, an innocuous von Frey filament (bending force 0.7 mN) was applied 3 times at separate sites oriented radially at a distance of 7 mm from the histamine injection site, and the presence or absence of a hindlimb scratch bout following each stimulus was noted (maximum alloknesis score = 3). The number of histamine- or vehicle-evoked hindlimb scratch bouts directed to the injection site (not associated with the von Frey stimulus) was counted after the experiment by reviewing the videotape.
) in the nape of the neck, the mouse was placed into the recording arena and videotaped for 30 min. At 5-min intervals, an innocuous von Frey filament (bending force 0.7 mN) was applied 3 times at separate sites oriented radially at a distance of 7 mm from the histamine injection site, and the presence or absence of a hindlimb scratch bout following each stimulus was noted (maximum alloknesis score = 3). The number of histamine- or vehicle-evoked hindlimb scratch bouts directed to the injection site (not associated with the von Frey stimulus) was counted after the experiment by reviewing the videotape.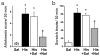
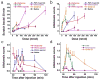
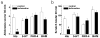

References
-
- Akiyama T, Carstens MI, Carstens E. Differential itch- and pain-related behavioral responses and micro-opoid modulation in mice. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010a;90:575–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

