Cholinesterase inhibitors for dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson's disease dementia and cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 22419314
- PMCID: PMC8985413
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006504.pub2
Cholinesterase inhibitors for dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson's disease dementia and cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: Previous Cochrane reviews have considered the use of cholinesterase inhibitors in both Parkinson's disease with dementia (PDD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). The clinical features of DLB and PDD have much in common and are distinguished primarily on the basis of whether or not parkinsonism precedes dementia by more than a year. Patients with both conditions have particularly severe deficits in cortical levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Therefore, blocking its breakdown using cholinesterase inhibitors may lead to clinical improvement.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy, safety and tolerability of cholinesterase inhibitors in dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), Parkinson's disease with dementia (PDD), and cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease falling short of dementia (CIND-PD) (considered as separate phenomena and also grouped together as Lewy body disease).
Search methods: The trials were identified from a search of ALOIS, the Specialised Register of the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group (on 30 August 2011) using the search terms Lewy, Parkinson, PDD, DLB, LBD. This register consists of records from major healthcare databases (MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, CINAHL) and many ongoing trial databases and is updated regularly.Reference lists of relevant studies were searched for additional trials.
Selection criteria: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials assessing the efficacy of treatment with cholinesterase inhibitors in DLB, PDD and cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease (CIND-PD).
Data collection and analysis: Data were extracted from published reports by one review author (MR). The data for each 'condition' (that is DLB, PDD or CIND-PD) were considered separately and, where possible, also pooled together. Statistical analysis was conducted using Review Manager version 5.0.
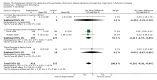
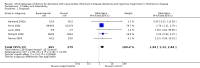
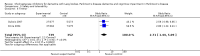
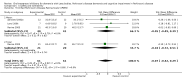
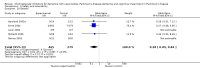
Main results: Six trials met the inclusion criteria for this review, in which a total of 1236 participants were randomised. Four of the trials were of a parallel group design and two cross-over trials were included. Four of the trials included participants with a diagnosis of Parkinson's disease with dementia (Aarsland 2002a; Dubois 2007; Emre 2004; Ravina 2005), of which Dubois 2007 remains unpublished. Leroi 2004 included patients with cognitive impairment and Parkinson's disease (both with and without dementia). Patients with dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) were included in only one of the trials (McKeith 2000).For global assessment, three trials comparing cholinesterase inhibitor treatment to placebo in PDD (Aarsland 2002a; Emre 2004; Ravina 2005) reported a difference in the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study-Clinical Global Impression of Change (ADCS-CGIC) score of -0.38, favouring the cholinesterase inhibitors (95% CI -0.56 to -0.24, P < 0.0001).For cognitive function, a pooled estimate of the effect of cholinesterase inhibitors on cognitive function measures was consistent with the presence of a therapeutic benefit (standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.34, 95% CI -0.46 to -0.23, P < 0.00001). There was evidence of a positive effect of cholinesterase inhibitors on the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in patients with PDD (WMD 1.09, 95% CI 0.45 to 1.73, P = 0.0008) and in the single PDD and CIND-PD trial (WMD 1.05, 95% CI 0.42 to 1.68, P = 0.01) but not in the single DLB trial.For behavioural disturbance, analysis of the pooled continuous data relating to behavioural disturbance rating scales favoured treatment with cholinesterase inhibitors (SMD -0.20, 95% CI -0.36 to -0.04, P = 0.01).For activities of daily living, combined data for the ADCS and the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) activities of daily living rating scales favoured treatment with cholinesterase inhibitors (SMD -0.20, 95% CI -0.38 to -0.02, P = 0.03).For safety and tolerability, those taking a cholinesterase inhibitor were more likely to experience an adverse event (318/452 versus 668/842; odds ratio (OR) 1.64, 95% CI 1.26 to 2.15, P = 0.0003) and to drop out (128/465 versus 45/279; OR 1.94, 95% CI 1.33 to 2.84, P = 0.0006). Adverse events were more common amongst those taking rivastigmine (357/421 versus 173/240; OR 2.28, 95% CI 1.53 to 3.38, P < 0.0001) but not those taking donepezil (311/421 versus 145/212; OR 1.24, 95% CI 0.86 to 1.80, P = 0.25). Parkinsonian symptoms in particular tremor (64/739 versus 12/352; OR 2.71, 95% CI 1.44 to 5.09, P = 0.002), but not falls (P = 0.39), were reported more commonly in the treatment group but this did not have a significant impact on the UPDRS (total and motor) scores (P = 0.71). Fewer deaths occurred in the treatment group than in the placebo group (4/465 versus 9/279; OR 0.28, 95% CI 0.09 to 0.84, P = 0.03).
Authors' conclusions: The currently available evidence supports the use of cholinesterase inhibitors in patients with PDD, with a positive impact on global assessment, cognitive function, behavioural disturbance and activities of daily living rating scales. The effect in DLB remains unclear. There is no current disaggregated evidence to support their use in CIND-PD.
Conflict of interest statement
RMcS has received financial support to attend conferences from Eisai, Shire and Novartis, all marketers of cholinesterase inhibitors, more than five years ago. Within the last two years, his institution has received funding for his activities as a local PL for a Novartis study of rivastigmine patch versus tablets in Parkinson's disease dementia.
Figures
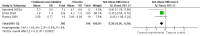































Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006504
References
References to studies included in this review
Aarsland 2002a {published data only}
Dubois 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Dubois B, Tolosa E, Kulisevsky J, Reichman H, Jones R, Burn D, et al. Efficacy and safety of donepezil in the treatment of Parkinson's disease patients with dementia. Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease Congress, Salzburg. 2007.
Emre 2004 {published data only}
-
- Burn D, Emre M, McKeith I. Reponse to rivastigmine in patients with and without visual hallucinations in dementia associated with Parkinson's disease (EXPRESS study group). 57th Annual meeting American Academy of Neurology. April 2005. [http:www.abstracts2view.com/aan/]
-
- Burn D, Emre M, McKeith I, Deyn PP, Aarsland D, Hsu C, et al. Effects of rivastigmine in patients with and without visual hallucinations in dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2006; Vol. 21, issue 11:1899‐907. - PubMed
-
- Dujardin K, Devos D, Duhem S, Destee A, Marie R‐M, Durif F, et al. Utility of the Mattis dementia rating scale to assess the efficacy of rivastigmine in dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neurology 2006; Vol. 253, issue 9:1154‐9. - PubMed
-
- Emre M, Aarsland D, Albanese A, Byrne EJ, Deuschl G, DeDeyn PP, et al. Rivastigmine for dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2004;351:2509‐18. - PubMed
-
- Emre M, Onofrj M, Tekin S, Quarg P, Lane R, Express Study Group. Benefits of rivastigmine in Parkinson's disease dementia: Results from the EXPRESS study. Neurobiology of Aging 2004;25 Suppl 2:19.
Leroi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Leroi I, Brandt J, Reich SG, Lyketsos CG, Grill S, Thompson R, Marsh L. Randomized placebo‐controlled trial of donepezil in cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2004;19(1):1‐8. - PubMed
McKeith 2000 {published data only}
-
- Byrne J. Treatment of Lewy body dementia with Exelon. National Research Register 2000. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Ser T. Efficacy of cholinesterase inhibitors in lewy body dementia. Sixth International Stockholm/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer Therapy; 5‐8 April 2000, Stockholm, Sweden 2000:51.
-
- Ser T, McKeith I, Anand R, Cicin‐Sain A, Ferrara R, Spiegel R. Dementia with Lewy bodies: findings from an international multicentre study. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2000;15(11):1034‐45. - PubMed
-
- McKeith I, Ser T, Anand R, et al. Rivastigmine provides symptomatic benefit in dementia with Lewy bodies: findings from a placebo‐controlled international multicenter study. Neurology 2000e; Vol. 54 Suppl 3:A450.
-
- McKeith I, Ser T, Spano P, Emre M, Wesnes K, Anand R, et al. Efficacy of rivastigmine in dementia with Lewy bodies: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled international study. Lancet 2000f; Vol. 356, issue 9247:2031‐6. - PubMed
Ravina 2005 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Aarsland 2002 {published data only}
-
- Aarsland D. Galantamine for Parkinson's disease with dementia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;12 Suppl:378‐9.
-
- Aarsland D, Hutchinson M, Larsen JP. Cognitive, psychiatric and motor response to galantamine in Parkinson's disease with dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;18(10):937‐41. - PubMed
Adler 2011 {published data only}
-
- Adler G, Christenn M, Bektas M, Ko‐Inoshishi Y, Kupsch A, Scholz E, et al. Rivastigmine treatment in Parkinson's disease dementia: short‐term cholinergic effects are correlated with six‐month treatment response. Alzheimer's and Dementia. Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. 16‐21 July 2011. Conference Publication 2011; Vol. 7 Suppl 1, issue 4:776.
Anand 2000 {published data only}
-
- Anand R, Enz A, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Effects of rivastigmine extend beyond symptomatic treatment in patients with Alzheimer's disease(AD): new clinical studies. Sixth International Stockholm/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer Therapy; April 5‐8, 2000; Stockholm, Sweden 2000:29.
Barone 2008 {published data only}
-
- Barone P, Burn DJ, Laar T, Hsu C, Poewe W, Lane RM. Rivastigmine versus placebo in hyperhomocysteinemic Parkinson's disease dementia patients. Movement Disorders 2008; Vol. 23, issue 11:1532‐40. - PubMed
Barone 2010 {published data only}
-
- Barone P, Deyn P, Emre M, Kulisevsky J, Poewe W, Pourcher E, et al. Baseline data from a long‐term safety study of rivastigmine capsules and patch in mild to moderate Parkinson's disease dementia. Movement Disorders. Conference: 14th International Congress of Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders Buenos Aires Argentina. 13‐17 June 2010. Conference Publication 2010; Vol. 25 Suppl:486‐7.
Bergman 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bergman J, Lerner V. Successful use of donepezil for the treatment of psychotic symptoms in patients with Parkinson's disease. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2002;25(2):107‐10. - PubMed
Bergman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bergman J, Brettholz I, Shneidman M, Lerner V. Donepezil as add‐on treatment of psychotic symptoms in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer's type. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2003;26(2):88‐92. - PubMed
Beversdorf 2004 {published data only}
-
- Beversdorf DQ, Warner JL, Davis RA, Sharma UK, Nagaraja HN, Scharre DW. Donepezil in the treatment of dementia with Lewy bodies. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2004;12(5):542‐4. - PubMed
Brashear 2004 {published data only}
-
- Brashear A, Kuhn ER, Lane KA, Farlow MR, Unverzagt FW. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial of donepezil in patients with Parkinson's disease and related dementia. Neurology 2004;62(7 Suppl):5.
Chung 2010 {published data only}
Cummings 2010 {published data only}
-
- Cummings J, Emre M, Aarsland D, Tekin S, Dronamraju N, Lane R. Effects of rivastigmine in Alzheimer's disease patients with and without hallucinations. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2010; Vol. 20, issue 1:301‐11. - PubMed
De Deyn 2011 {published data only}
-
- Deyn P, Poewe W, Barone P, Emre M, Kulisevsky J, Pourcher E, et al. Results of a long‐term safety study of rivastigmine capsules and patch in patients with mild to moderate dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. Neurodegenerative Diseases. Conference: 10th International Conference AD/PD ‐ Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases: Advances, Concepts and New Challenges Barcelona Spain. 9‐13 March 2011. Conference Publication 2011; Vol. 8.
Fabbrini 2002 {published data only}
-
- Fabbrini G, Barbanti P, Aurilia C, Pauletti C, Lenzi GL, Meco G. Donepezil in the treatment of hallucinations and delusions in Parkinson's disease. Neurological Sciences 2002;23:41‐3. - PubMed
Fogelson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Fogelson N, Kogan E, Korczyn AD, Giladi N, Shabtai H, Neufeld MY. Effects of rivastigmine on the quantitative EEG in demented parkinsonian patients. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2003;107(4):252‐5. - PubMed
Foy 2000 {published data only}
-
- Foy C. The non‐dopaminergic neuropharmacology of idiopathic Parkinson's Disease. Thesis submitted in fulfilment for a Doctor of Philosophy, Section of Clinical Neurology, University of Sheffield (accessed from the British Library) 2000.
-
- Grunewald RA. Investigation of the effects of rivastigmine on cognition in Parkinson's disease. National Research Register 1999.
Fujita 2010 {published data only}
-
- Fujita Y, Takebayash M. Efficacy of low‐dose donepezil for visual hallucinations in a patient with dementia with Lewy bodies. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2010; Vol. 64, issue 3:336. - PubMed
Giladi 2003 {published data only}
-
- Giladi N, Shabtai H, Gurevich T, Benbunan B, Anca M, Korczyn AD. Rivastigmine for dementia in patients with Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2003;108:368‐73. - PubMed
Gustavsson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gustavsson A, Putt R, Jonsson L, McShane R. Economic evaluation of cholinesterase inhibitor therapy for dementia: comparison of Alzheimer's disease and Dementia with Lewy bodies. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2009; Vol. 24, issue 10:1072‐8. - PubMed
Hutchinson 1996 {published data only}
Korczyn 2001 {published data only}
-
- Korczyn AD, Shabati H, Benbunan B, Gurevich T, Anca M, Sidis S, Giladi N. The effect of treatment with rivastigmine (Exelon) on cognitive functions of patients with dementia and Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2001;7 Suppl:61.
Lanctot 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lanctot KL, Hermann N. Donepezil for behavioural disorders associated with Lewy bodies: a case series. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2000;15:183‐8. - PubMed
Linsarazo 2005 {published data only}
-
- Linsarozo G, Lasa A, Blercom N. Efficacy and safety of donepezil in cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: a pilot study. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2005;28(4):176‐8. - PubMed
Litvinenko 2008 {published data only}
-
- Litvinenko IV, Odinak MM, Mogil'naya VI, Emelin AYU. Efficacy and safety of galantamine (Reminyl) for dementia in patients with Parkinson's disease (an open controlled trial). Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology 2008; Vol. 38, issue 9:937‐45. - PubMed
McKeith 2000a {published data only}
-
- McKeith IG. A pilot study into the effects of donepezil on cognitive impairment and neuropsychiatric features in patients with dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease. National Research Register 2000a.
McLaren 2003 {published data only}
-
- McLaren AT, Allen J, Murray A, Ballard CG, Kenny RA. Cardiovascular effects of donepezil in patients with dementia. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2003;15:183‐8. - PubMed
Minett 2003 {published data only}
-
- Minett TS, Thomas A, Wilkinson LM, Daniel SL, Sanders J, Richardson J, et al. What happens when donepezil is suddenly withdrawn? An open label trial in dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease with dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;18(11):988‐93. - PubMed
Mori 2006 {published data only}
-
- Mori S, Mori E, Iseki E, Kosaka K. Efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with dementia with Lewy bodies: preliminary findings from an open‐label study. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2006;60(2):190‐5. - PubMed
Olin 2010a {published data only}
-
- Olin JT, Bhatnagar V, Reyes P, Koumaras B, Meng X, et al. Safety and tolerability of rivastigmine capsule with memantine in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease: A 26‐week, open‐label, prospective trial (Study ENA713B US32). International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2010; Vol. 25, issue 4:419‐26. - PubMed
Pakrasi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Pakrasi S, Thomas A, Mosimann UP, Cousins DA, Burn DJ, O'Brien JT, McKeith IG. Cholinesterase inhibitors in advanced dementia with Lewy bodies: increase or stop?. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2006;21(8):719‐21. - PubMed
Reading 2001 {published data only}
-
- Reading PJ, Luce AK, McKeith IG. Rivastigmine in the treatment of Parkinson's psychosis and cognitive impairment: preliminary findings from an open trial. Movement Disorders 2001;16:1171‐95. - PubMed
Rektorova 2004 {published data only}
-
- Rektorova I. Effect of donepezil on dementia in Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease: a pilot study [Ucinek donepezilu na demenci u parkinonovy nemoci a alzheimerovy nemoci. pilotni studie]. Ceska a Slovenska Neurologie a Neurchirurgie 2004;67(5):359‐63.
Rosengarten 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rosengarten B, Dannhardt V, Burr O, Pohler M, Rosengarten S, Oechsner M, et al. Neurovascular coupling in Parkinson's disease patients: effects of dementia and acetylcholinesterase inhibitor treatment. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2010; Vol. 22, issue 2:415‐21. - PubMed
Samuel 2000 {published data only}
-
- Samuel W, Caligiuri M, Galasko D, Lacro J, Marini M, McClure FS, et al. Better cognitive and psychopathologic response to donepezil in patients prospectively diagnosed as dementia with Lewy bodies: A preliminary study. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2000; Vol. 15, issue 9:794‐802. - PubMed
Satoh 2010 {published data only}
-
- Satoh M, Ishikawa H, Meguro K, Kasuya M, Ishii H, Yamauchi S. Improved visual hallucination by donepezil and occipital glucose metabolism in dementia with Lewy bodies: the Osaki‐Tajiri project. European Neurology 2010; Vol. 64, issue 6:337‐44. - PubMed
Thomas 2005 {published data only}
-
- Thomas AJ, Burns A, Rowan EN, Littlewood E, Newby J, Cousins D, et al. A comparison of the efficacy of donepezil in Parkinson's disease with dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2005;20(10):938‐44. - PubMed
Touchon 2006a {published data only}
-
- Touchon J, Bergman H, Bullock R, Rapatz G, Nagel J, Lane R. Response to rivastigmine or donepezil in Alzheimer's patients with symptoms suggestive of concomitant Lewy body pathology. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2006;22(1):49. - PubMed
Touchon 2006b {published data only}
-
- Touchon J, Bergman H, Bullock R. Erratum: Response to rivastigmine or donepezil in Alheimer's patients with symptoms suggestive of concomitant Lewy body pathology. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2006;22(1):45. - PubMed
Van Laar 2001 {published data only}
-
- Laar T, Vries JJ, Nakhosteen A, Leenders KL. Rivastigmine as anti‐psychotic treatment in patients with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2001;7 Suppl:73.
Vasile 2010a {published data only}
-
- Vasile D, Vasiliu O, Vasile ML, Terpan M, Grigorescu G, Bogdan V, et al. Comparative efficacy of cholinesterase inhibitors in dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. European Neuropsychopharmacology. Conference: 23rd European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, ECNP Congress Amsterdam, Netherlands. 28 August to 1 September 2010. Conference Publication 2010; Vol. 20 Suppl:553‐4.
Vasile 2010b {published data only}
-
- Vasile D, Vasiliu O. Management of cognitive symptoms in dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. Proceedings of the World Medical Conference 2010:284‐6.
Walker 2000b {published data only}
-
- Walker Z. Lewy body dementia: The investigation of pre and post synaptic dopaminergic receptors with SPET. NRR 2000. [MEDLINE: ]
Werber 2001 {published data only}
-
- Werber EA, Rabey JM. The beneficial effect of cholinesterase inhibitors on patients suffering from Parkinson's disease and dementia. Journal of Neural Transmission 2001;108(11):1319‐25. - PubMed
Wilcock 2000 {published data only}
-
- Wilcock GK. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomised, parallel group phase IIa study of the efficacy and safety of a novel therapy in the treatment of behavioural and psychological symptoms in subjects with dementia with Lewy bodies. National Research Register 2000e.
References to ongoing studies
Anon 2004a {published data only}
-
- Anon. Donepezil to treat dementia in Parkinson's disease. ClinicalTrials.gov 2004.
Anon 2007a {published data only}
-
- Anon. Double‐blind study of E2020 in patients with dementia with Lewy bodies ‐ Phase II. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007.
Anon 2011 {published data only}
-
- Anon. A study of E2020 in patients with dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), followed by a long‐term extension phase ‐ Phase III. ClinicalTrials.gov 2011.
Burn 2009 {published data only}
-
- Burn DJ. Multi‐centre UK study of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor donepezil in early dementia associated with Parkinson's disease (MUSTARDD‐PD). ClinicalTrials.gov: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01014858 2009.
Kurlan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Kuran R. Treatment of agitation/psychosis in dementia/parkinsonism. Alzheimer's Disease Education and Referral Centre (ADEAR) 2003.
Marion 2003 {published data only}
-
- Marion MH. An open 24 week prospective, randomised, double‐blind placebo controlled parallel group study of efficacy, tolerability and safety of 3‐12mg/day of Exelon and Exelon (rivastigmine) capsules in patients with Parkinson's disease dementia. National Research Register 2003.
Additional references
Aarsland 2003
-
- Aarsland D, Andersen K, Larsen JP, Lolk A, Kragh‐Sorensen P. Prevalence and characteristics of dementia in Parkinson disease: an 8‐year prospective study. Archives of Neurology 2003;60:387‐92. - PubMed
Aarsland 2005
-
- Aarsland D, Zaccai J, Brayne C. A systematic review of prevalence studies of dementia in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2005;20:1255‐63. - PubMed
Ballard 2006
-
- Ballard C, Ziabreva I, Perry R, Larsen JP, O'Brien J, McKeith I, et al. Differences in neuropathologic characteristics across the Lewy body dementia spectrum. Neurology 2006;67(11):1931‐4. - PubMed
Barr 1996
-
- Barr A, Brandt J. Word‐list generation deficits in dementia. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology 1996;18:810‐22. - PubMed
Bedard 2003
-
- Bedard MA, Agid Y, Chouinard S, et al. Mental and Behavioural dysfunction in movement disorders. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 2003.
Beery 1989
-
- Beery KE. Revised Administration, Scoring and Teaching Manual for the Developmental Test of Visual‐Motor Integration. Cleveland: Modern Curriculum Press, 1989.
Bostrom 2006
-
- Bostrom F, Jonsson L, Minthon L, Londos E. Patients with Lewy body dementia use more resources than those with Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2006; Vol. 22, issue 8:713‐9. - PubMed
Braak 2006
-
- Braak H, Rub U, Tredici K. Cognitive decline correlates with neuropathological stage in Parkinson's disease. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2006;248(1‐2):255‐8. - PubMed
Brandt 2001
-
- Brandt J, Benedict RHB. Hopkins Verbal Learning Test‐Revised, Professional Manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc., 2001.
Burn 2003
-
- Burn DJ, McKeith IG. Current treatment of dementia with Lewy bodies and dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2003;18 Suppl 6:72‐9. - PubMed
Burn 2006
-
- Burn DJ. Cortical Lewy body disease and Parkinson's disease dementia. Current Opinions in Neurology 2006;19(6):572‐9. - PubMed
Cummings 1994
-
- Cummings JL, Mega M, Gray K, Rosenburg‐Thompson S, Carusi DA, Gornbein J. The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: Comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology 1994;44:2308‐13. - PubMed
Delis 2001
-
- Delis DC, Kaplan E, Kramer JH. Delis‐Kaplan executive function system. San Antonio, Tex.: Psychological Corporation, 2001.
Dubois 1997
-
- Dubois B, Pillon B. Cognitive deficits in Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neurology 1997;244:2‐8. - PubMed
Fahn 1987
-
- Fahn S, Elton RS, Members of the UPDRS Develpment Committee. Unified Parkinson's disease rating scale. In: Fahn S, Marsden CD, Goldstein M editor(s). Recent Developments in Parkinson's Disease II. New York: Macmillan, 1987:153‐63.
Folstein 1975
-
- Folstein NF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini‐Mental State: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1975;12:189‐98. - PubMed
Galasko 1997
-
- Galasko D, Bennett D, Sano M, et al. An inventory to assess activities of daily living for clinical trials in Alzheimer's disease. The Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 1997;11 Suppl 2:533‐9. - PubMed
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
Jellinger 1994
-
- Jellinger KA, Bancher CH, Fischer P. Neuropathological correlates of mental dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. In: Wolters EC, Scheltens PH editor(s). Mental Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease. Dordrecht: ICG Printing, 1994:141‐61.
Lee 2006
-
- Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Mechanisms of Parkinson's disease linked to pathological alpha‐synuclein: new targets for drug discovery. Neuron 2006;52(1):33‐8. - PubMed
Lippa 1998
-
- Lippa CF, Johnson R, Smith TW. The medial temporal lobe in dementia with Lewy bodies: a comparative study with Alzheimer's disease. Annals of Neurology 1998;43(1):102‐6. - PubMed
Maidment 2006
Manos 1994
-
- Manos PJ, Wu R. The ten point clock drawing test: a quick screen and grading method for cognitive impairment in medical and surgical patients. International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine 1994;24:229‐44. - PubMed
Mattis 1988
-
- Mattis S. Dementia Rating Scale (DRS) Professional Manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc., 1988.
McKeith 1992
McKeith 1996
-
- McKeith IG, Galasko D, Kosaka K, Perry EK, Dickson DW, Hansen LA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology 1996;47:1113‐24. - PubMed
McKeith 2005
-
- McKeith IG, Dickson DW, Lowe J, Emre M, O’Brien JT, Feldman H, et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies. Third report of the DLB consortium. Neurology 2005;65:1863‐72. - PubMed
Nakano 1984
-
- Nakano I, Hirano A. Parkinson's disease: neuron loss in the nucleus basalis without concomitant Alzheimer's disease. Annals of Neurology 1984;15:415‐8. - PubMed
Olanow 2006
-
- Olanow CW, McNaught KS. Ubiquitin‐proteasome system and Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2006;21(11):1806‐23. - PubMed
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:790‐812.
Perry 1994
-
- Perry EK, Haroutunian V, Davis KL, et al. Neocortical cholinergic activities differentiate Lewy body dementia from classical Alzheimer's disease. NeuroReport 1994;5(7):747‐9. - PubMed
Reitan 1958
-
- Reitan RM. Validity of the Trail Making Test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Perceptual and Motor Skills 1958;8:271‐6.
Rosen 1984
-
- Rosen WG, Mohs RC, Davis K. A new rating scale for Alzheimer's disease. American Journal of Psychiatry 1984;141:1356‐64. - PubMed
Schneider 1997
-
- Schneider LS, Olin JT, Doody RS, et al. Validity and reliability of the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study ‐ Clinical Global Impression of Change. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 1997;11 Suppl 2:22‐32. - PubMed
Schretlen 1997
-
- Schretlen D. Brief Test of Attention Professional Manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc., 1997.
Simpson 1991
-
- Simpson PM, Surmon DJ, Wesnes KA, Wilcock GK. The cognitive assessment system for the demented patients: a validation study. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1991;6:95‐102.
Wild 2003
Williams 2009
-
- Williams SS, Williams J, Combrinck M, Christie S, Smith AD, McShane R. Olfactory impairment is more marked in patients with mild dementia with Lewy bodies than those with mild Alzheimer disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 2009;80(6):667‐70. - PubMed
Zaccai 2005
-
- Zaccai J, McCracken C, Brayne C. A systematic review of prevalence and incidence studies of dementia with Lewy bodies. Age and Ageing 2005;34:561‐6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

