Erythropoietin treatment enhances muscle mitochondrial capacity in humans
- PMID: 22419911
- PMCID: PMC3299978
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00050
Erythropoietin treatment enhances muscle mitochondrial capacity in humans
Abstract
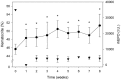
Erythropoietin (Epo) treatment has been shown to induce mitochondrial biogenesis in cardiac muscle along with enhanced mitochondrial capacity in mice. We hypothesized that recombinant human Epo (rhEpo) treatment enhances skeletal muscle mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) capacity in humans. In six healthy volunteers rhEpo was administered by sub-cutaneous injection over 8 weeks with oral iron (100 mg) supplementation taken daily. Mitochondrial OXPHOS was quantified by high-resolution respirometry in saponin-permeabilized muscle fibers obtained from biopsies of the vastus lateralis before and after rhEpo treatment. OXPHOS was determined with the mitochondrial complex I substrates malate, glutamate, pyruvate, and complex II substrate succinate in the presence of saturating ADP concentrations, while maximal electron transport capacity (ETS) was assessed by addition of an uncoupler. rhEpo treatment increased OXPHOS (from 92 ± 5 to 113 ± 7 pmol·s(-1)·mg(-1)) and ETS (107 ± 4 to 143 ± 14 pmol·s(-1)·mg(-1), p < 0.05), demonstrating that Epo treatment induces an upregulation of OXPHOS and ETS in human skeletal muscle.
Keywords: humans; mitochondria; muscle; oxidative phosphorylation; rhEPO.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson E. J., Lustig M. E., Boyle K. E., Woodlief T. L., Kane D. A., Lin C. T., Price J. W., III, Kang L., Rabinovitch P. S., Szeto H. H., Houmard J. A., Cortright R. N., Wasserman D. H., Neufer P. D. (2009). Mitochondrial H2O2 emission and cellular redox state link excess fat intake to insulin resistance in both rodents and humans. J. Clin. Invest. 119, 573–58110.1172/JCI37048 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

