Cutaneous side effects of new antitumor drugs: clinical features and management
- PMID: 22419954
- PMCID: PMC3301977
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2012.0133
Cutaneous side effects of new antitumor drugs: clinical features and management
Abstract
Background: Many new antitumor drugs have been approved in recent years. Their side-effect profiles are distinct from those of older drugs, and their adverse effects are sometimes highly specific, particularly with respect to the skin.
Methods: This article is based on articles retrieved by a selective search in Medline and the database of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), as well as on the authors' personal experience.
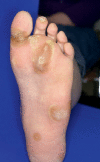
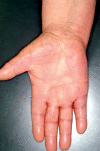
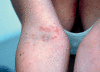
Results: Cutaneous adverse effects are among the more common adverse effects of new antitumor drugs: they occur in up to 34% of patients receiving multikinase inhibitors, up to 90% of those receiving selective tyrosine kinase inhibitors (such as EGFR or mutant BRAF inhibitors), and up to 68% of those receiving immunotherapeutic agents (such as CTLA4 inhibitors). These adverse effects can be correlated with therapeutic benefit, but they can also be treatment-limiting because of their severity or visibility.
Conclusion: The recognition and proper management of cutaneous adverse effects is an important part of treatment with new antitumor drugs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Cutaneous side effects of anti-tumor therapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitors].Hautarzt. 2014 Jul;65(7):582-9. doi: 10.1007/s00105-013-2733-8. Hautarzt. 2014. PMID: 24903029 German.
-
Cutaneous Adverse Events of New Anti-melanoma Therapies: Classification and Management.Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017 Jan-Feb;108(1):6-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2016.05.019. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017. PMID: 27642030 Review. English, Spanish.
-
Dermatologic adverse events to chemotherapeutic agents, Part 2: BRAF inhibitors, MEK inhibitors, and ipilimumab.Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2014 Mar;33(1):40-8. doi: 10.12788/j.sder.0061. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2014. PMID: 25037257 Review.
-
[Cutaneous side effects of the multikinase inhibitors sorafenib and sunitinib].Hautarzt. 2010 Aug;61(8):662-7. doi: 10.1007/s00105-010-1942-7. Hautarzt. 2010. PMID: 20631979 Review. German.
-
Cutaneous Complications of Targeted Melanoma Therapy.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2016 Nov;17(11):57. doi: 10.1007/s11864-016-0434-0. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27645330 Review.
Cited by
-
Serial low doses of sorafenib enhance therapeutic efficacy of adoptive T cell therapy in a murine model by improving tumor microenvironment.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 15;9(10):e109992. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109992. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25333973 Free PMC article.
-
[Undesired cutaneous adverse drug reactions: What is new?].Internist (Berl). 2012 Aug;53(8):917-23. doi: 10.1007/s00108-012-3057-y. Internist (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22814563 German.
-
[Common treatment diagnoses in dermatological emergency services].Hautarzt. 2022 Feb;73(2):161-170. doi: 10.1007/s00105-021-04930-1. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Hautarzt. 2022. PMID: 35061056 Review. German.
-
Mechanism of Lethal Skin Toxicities Induced by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors and Related Treatment Strategies.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 10;12:804212. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.804212. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35223483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silkworm Pupa Protein Hydrolysate Induces Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis and S Phase Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 28;19(4):1013. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041013. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29597296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, Normanno N. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1995;19:183–232. - PubMed
-
- Potthoff K, Hofheinz R, Hassel JC, et al. Interdisciplinary management of EGFR-inhibitor-induced skin reactions: a German expert opinion. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:524–535. - PubMed
-
- Wollenberg A, Kroth J, Hauschild A, Dirschka T. Hautreaktionen unter EGFR-Inhibitoren - Klinik und Management. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2010;135:149–154. - PubMed
-
- Gutzmer R, Becker JC, Enk A, et al. Management kutaner Nebenwirkungen von FGFR-Inhibitoren: Empfehlungen eines deutschen Expertengremiums für den primär behandelnden Arzt. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2011;9:195–203. - PubMed
-
- Wollenberg A, Moosmann N, Klein E, Katzer K. A tool for scoring of acneiform skin eruptions induced by EGF receptor inhibition. Exp Dermatol. 2008;17:790–792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

