Under the radar: how unexamined biases in decision-making processes in clinical interactions can contribute to health care disparities
- PMID: 22420809
- PMCID: PMC3483919
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2011.300601
Under the radar: how unexamined biases in decision-making processes in clinical interactions can contribute to health care disparities
Abstract
Several aspects of social psychological science shed light on how unexamined racial/ethnic biases contribute to health care disparities. Biases are complex but systematic, differing by racial/ethnic group and not limited to love-hate polarities. Group images on the universal social cognitive dimensions of competence and warmth determine the content of each group's overall stereotype, distinct emotional prejudices (pity, envy, disgust, pride), and discriminatory tendencies. These biases are often unconscious and occur despite the best intentions. Such ambivalent and automatic biases can influence medical decisions and interactions, systematically producing discrimination in health care and ultimately disparities in health. Understanding how these processes may contribute to bias in health care can help guide interventions to address racial and ethnic disparities in health.
Figures
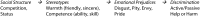
References
-
- National Center for Health Statistics Healthy People 2010. Hyattsville, MD: Government Printing Office; 2011
-
- Mead H, Cartwright-Smith L, Jones K, Ramos C, Woods C, Siegel B. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in U.S. Healthcare: A Chartbook. Winston-Salem, NC: Wake Forest University School of Medicine
-
- Penner LA, Albrecht TL, Orom H, Coleman DK, Underwood W., III Health and health care disparities. : Dovidio JF, Hewstone M, Glick P, Esses VM, Handbook of Prejudice, Stereotyping, and Discrimination. London, UK: Sage; 2010:472–490
-
- Smedley B, Stith A, Nelson A, Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

