The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: a mendelian randomisation analysis
- PMID: 22421340
- PMCID: PMC3316968
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60110-X
The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: a mendelian randomisation analysis
Abstract
Background: A high circulating concentration of interleukin 6 is associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease. Blockade of the interleukin-6 receptor (IL6R) with a monoclonal antibody (tocilizumab) licensed for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis reduces systemic and articular inflammation. However, whether IL6R blockade also reduces risk of coronary heart disease is unknown.
Methods: Applying the mendelian randomisation principle, we used single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the gene IL6R to evaluate the likely efficacy and safety of IL6R inhibition for primary prevention of coronary heart disease. We compared genetic findings with the effects of tocilizumab reported in randomised trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
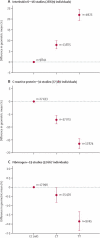
Findings: In 40 studies including up to 133,449 individuals, an IL6R SNP (rs7529229) marking a non-synonymous IL6R variant (rs8192284; p.Asp358Ala) was associated with increased circulating log interleukin-6 concentration (increase per allele 9·45%, 95% CI 8·34-10·57) as well as reduced C-reactive protein (decrease per allele 8·35%, 95% CI 7·31-9·38) and fibrinogen concentrations (decrease per allele 0·85%, 95% CI 0·60-1·10). This pattern of effects was consistent with IL6R blockade from infusions of tocilizumab (4-8 mg/kg every 4 weeks) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis studied in randomised trials. In 25,458 coronary heart disease cases and 100,740 controls, the IL6R rs7529229 SNP was associated with a decreased odds of coronary heart disease events (per allele odds ratio 0·95, 95% CI 0·93-0·97, p=1·53×10(-5)).
Interpretation: On the basis of genetic evidence in human beings, IL6R signalling seems to have a causal role in development of coronary heart disease. IL6R blockade could provide a novel therapeutic approach to prevention of coronary heart disease that warrants testing in suitably powered randomised trials. Genetic studies in populations could be used more widely to help to validate and prioritise novel drug targets or to repurpose existing agents and targets for new therapeutic uses.
Funding: UK Medical Research Council; British Heart Foundation; Rosetrees Trust; US National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; Du Pont Pharma; Chest, Heart and Stroke Scotland; Wellcome Trust; Coronary Thrombosis Trust; Northwick Park Institute for Medical Research; UCLH/UCL Comprehensive Medical Research Centre; US National Institute on Aging; Academy of Finland; Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development; SANCO; Dutch Ministry of Public Health, Welfare and Sports; World Cancer Research Fund; Agentschap NL; European Commission; Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation; Swedish Research Council; Strategic Cardiovascular Programme of the Karolinska Institutet; Stockholm County Council; US National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; MedStar Health Research Institute; GlaxoSmithKline; Dutch Kidney Foundation; US National Institutes of Health; Netherlands Interuniversity Cardiology Institute of the Netherlands; Diabetes UK; European Union Seventh Framework Programme; National Institute for Healthy Ageing; Cancer Research UK; MacArthur Foundation.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00000611.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
The interleukin-6 pathway and atherosclerosis.Lancet. 2012 Mar 31;379(9822):1176-8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60361-4. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Lancet. 2012. PMID: 22421338 No abstract available.
-
Coronary artery disease: IL-6 signaling linked with CHD.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012 Apr 3;9(6):313. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2012.46. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22473076 No abstract available.
-
The interleukin 6 pathway and atherosclerosis.Lancet. 2012 Jul 28;380(9839):338. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61246-X. Lancet. 2012. PMID: 22841333 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- FS/07/011/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 NS039987/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM010098/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG08/008/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 081081/Z/06/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01 AG23522-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RG/04/003/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/09/022/26739/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900009C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- AG000954-06/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS042733/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/008/25291/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000954/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL036310/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A100_1003/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- FS 05/125/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G19/35/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RFP-NHLBI-WH-11-10/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- 064947/Z/01/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- C150/A5660/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0100222/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- AG1764406S1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG005152/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RR-024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 12076/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MC_U123092721/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- AG13196/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G8802774/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/08/013/25942/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0902037/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200625226C/PHS HHS/United States
- HHSN268200960009C/PHS HHS/United States
- N01HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127527198/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R37 AG013196/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0500877/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U123092720/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG023522/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL36310/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AR066486/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013196/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HS06516/HS/AHRQ HHS/United States
- G0802432/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG005152/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G1000718/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5215810-55000000041/PHS HHS/United States
- PG/07/133/24260/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 NS39987/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- C1298/A8362/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 NS42733/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000015/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- NHLBI 33014/PHS HHS/United States
- LM010098/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-65226/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/07/008/23674/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RG/10/12/28456/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

