Neuromuscular electrical stimulation for intensive care unit-acquired weakness: protocol and methodological implications for a randomized, sham-controlled, phase II trial
- PMID: 22421734
- PMCID: PMC3513483
- DOI: 10.2522/ptj.20110437
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation for intensive care unit-acquired weakness: protocol and methodological implications for a randomized, sham-controlled, phase II trial
Abstract
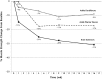
Background: As the population ages and critical care advances, a growing number of survivors of critical illness will be at risk for intensive care unit (ICU)-acquired weakness. Bed rest, which is common in the ICU, causes adverse effects, including muscle weakness. Consequently, patients need ICU-based interventions focused on the muscular system. Although emerging evidence supports the benefits of early rehabilitation during mechanical ventilation, additional therapies may be beneficial. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES), which can provide some muscular activity even very early during critical illness, is a promising modality for patients in the ICU.
Objective: The objectives of this article are to discuss the implications of bed rest for patients with critical illness, summarize recent studies of early rehabilitation and NMES in the ICU, and describe a protocol for a randomized, phase II pilot study of NMES in patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
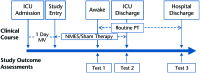
Design: The study was a randomized, sham-controlled, concealed, phase II pilot study with caregivers and outcome assessors blinded to the treatment allocation.
Setting: The study setting will be a medical ICU.
Participants: The study participants will be patients who are receiving mechanical ventilation for 1 day or more, who are expected to stay in the ICU for an additional 2 days or more, and who meet no exclusion criteria.
Intervention: The intervention will be NMES (versus a sham [control] intervention) applied to the quadriceps, tibialis anterior, and gastrocnemius muscles for 60 minutes per day.
Measurements: Lower-extremity muscle strength at hospital discharge will be the primary outcome measure.
Limitations: Muscle strength is a surrogate measure, not a patient-centered outcome. The assessments will not include laboratory, genetic, or histological measures aimed at a mechanistic understanding of NMES. The optimal duration or dose of NMES is unclear.
Conclusions: If NMES is beneficial, the results of the study will help advance research aimed at reducing the burden of muscular weakness and physical disability in survivors of critical illness.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00709124.
Figures


References
-
- Adhikari NK, Rubenfeld GD. Worldwide demand for critical care. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2011;17:620–625 - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554 - PubMed
-
- Wunsch H, Linde-Zwirble WT, Angus DC, et al. The epidemiology of mechanical ventilation use in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:1947–1953 - PubMed
-
- Zilberberg MD, de Wit M, Shorr AF. Accuracy of previous estimates for adult prolonged acute mechanical ventilation volume in 2020: update using 2000–2008 data. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:18–20 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

