The chemical complexity of cellular microtubules: tubulin post-translational modification enzymes and their roles in tuning microtubule functions
- PMID: 22422711
- PMCID: PMC3459347
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.21027
The chemical complexity of cellular microtubules: tubulin post-translational modification enzymes and their roles in tuning microtubule functions
Abstract
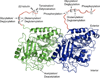
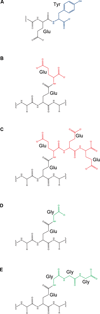
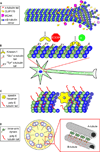
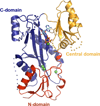
Cellular microtubules are marked by abundant and evolutionarily conserved post-translational modifications that have the potential to tune their functions. This review focuses on the astonishing chemical complexity introduced in the tubulin heterodimer at the post-translational level and summarizes the recent advances in identifying the enzymes responsible for these modifications and deciphering the consequences of tubulin's chemical diversity on the function of molecular motors and microtubule associated proteins.
Published 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Arce CA, Rodriguez JA, Barra HS, Caputo R. Incorporation of L-tyrosine, L-phenylalanine and L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine as single units into rat brain tubulin. Eur J Biochem. 1975;59(1):145–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

