Decoding in the absence of a codon by tmRNA and SmpB in the ribosome
- PMID: 22422985
- PMCID: PMC3763467
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1217039
Decoding in the absence of a codon by tmRNA and SmpB in the ribosome
Abstract
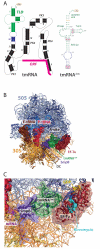
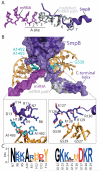
In bacteria, ribosomes stalled at the end of truncated messages are rescued by transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA), a bifunctional molecule that acts as both a transfer RNA (tRNA) and a messenger RNA (mRNA), and SmpB, a small protein that works in concert with tmRNA. Here, we present the crystal structure of a tmRNA fragment, SmpB and elongation factor Tu bound to the ribosome at 3.2 angstroms resolution. The structure shows how SmpB plays the role of both the anticodon loop of tRNA and portions of mRNA to facilitate decoding in the absence of an mRNA codon in the A site of the ribosome and explains why the tmRNA-SmpB system does not interfere with normal translation.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

