Update on the pathophysiology and management of idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- PMID: 22423118
- PMCID: PMC3544160
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2011-302029
Update on the pathophysiology and management of idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Abstract
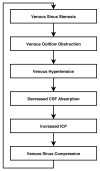
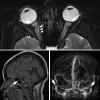
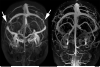
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is a disease of unknown aetiology, typically affecting young obese women, producing a syndrome of increased intracranial pressure without identifiable cause. Despite a large number of hypotheses and publications over the past decade, the aetiology is still unknown. Vitamin A metabolism, adipose tissue as an actively secreting endocrine tissue and cerebral venous abnormalities are areas of active study regarding the pathophysiology of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. There continues to be no evidence based consensus or formal guidelines regarding management and treatment of the disease. Treatment studies show that the diagnostic lumbar puncture is a valuable intervention beyond its diagnostic importance, and that weight management is critical. However, many questions remain regarding the efficacy of acetazolamide, CSF shunting procedures and cerebral transverse venous sinus stenting.
Figures
References
-
- Friedman DI, Jacobson DM. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology. 2002;59:1492–1495. - PubMed
-
- Friedman DI, Jacobson DM. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neuroophthalmol. 2004;24:138–145. - PubMed
-
- Digre KB. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. BMJ. 2010;341:c2836. - PubMed
-
- Kapoor KG. More than meets the eye? Redefining idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Int J Neurosci. 2010;120:471–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
