Rhabdomyolysis in a patient treated with linezolid for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis
- PMID: 22423128
- PMCID: PMC3404720
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cis293
Rhabdomyolysis in a patient treated with linezolid for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis
Abstract
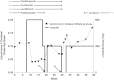
Prolonged use of linezolid was temporally and mechanistically associated with rhabdomyolysis in a patient being treated for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Careful laboratory monitoring of such subjects is important during prolonged linezolid therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Condos R, Hadgiangelis N, Leibert E, Jacquette G, Harkin T, Rom WN. Case series report of a linezolid-containing regimen for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Chest. 2008;134:187–92. - PubMed
-
- Yew WW, Leung CC. Antituberculosis drugs and hepatotoxicity. Respirology. 2006;11:699–707. - PubMed
-
- Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981;30:239–45. - PubMed
-
- Allison GW, Perla RJ, Belliveau PP, Angelis SM. Elevated creatine phosphokinase levels associated with linezolid therapy. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2009;66:1097–100. - PubMed
-
- Hsiao SH, Chang CM, Tsao CJ, Lee YY, Hsu MY, Wu TJ. Acute rhabdomyolysis associated with ofloxacin/levofloxacin therapy. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39:146–9. - PubMed

