Targeting the insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway in lung cancer: problems and pitfalls
- PMID: 22423264
- PMCID: PMC3296080
- DOI: 10.1177/1758834011427576
Targeting the insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway in lung cancer: problems and pitfalls
Abstract
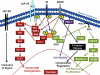
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) pathway is a complex pathway involving interactions between membrane-bound receptors, ligands, binding proteins, downstream effectors, and other receptor tyrosine kinase signaling cascades. The IGF pathway has been identified as a potential therapeutic target in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) based on the following provocative factors. Preclinical observations in NSCLC have shown that this pathway is involved in tumor cell proliferation, survival, and invasiveness. In addition, IGF-1R protein expression is found in a significant number of non-small cell tumor specimens. Initial therapeutic efforts involved the development of monoclonal antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors that target IGF-1R, a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase. Enthusiasm for targeting this pathway increased when a randomized phase II study showed that combining an anti-IGF-1R monoclonal antibody (figitumumab) with a platinum doublet resulted in a higher response rate and trends for superior progression-free survival and overall survival. Subsequently, a phase III study failed to confirm the promising results observed in the phase II trial. Currently, investigators are studying different monoclonal antibodies and tyrosine kinases targeting IGF-1R. In unselected patients, results presented thus far do not suggest efficacy of this agent. However, retrospective subgroup analyses suggest that circulating IGF-1 levels might identify patients who could benefit from treatment with an IGF-1R monoclonal antibody and may warrant further exploratory studies for predictive molecular markers. The purpose of this paper is to briefly discuss the IGF pathway and its relationship with other signaling pathways in lung cancer and to review the ongoing IGF clinical trials and efforts to identify predictive molecular markers.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor; figitumumab; insulin-like growth factor; insulin-like growth factor receptor; non-small cell lung cancer; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
MJF has served as an advisor for Bristol Myers Squibb and Genentech and received speaking honoraria from Lilly and Genentech. PB has served as an advisor for Genentech, Lilly, Bristol Myers Squibb.
Figures
References
-
- Baxter R.C., Martin J.L., Beniac V.A. (1989) High molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding complex. Purification and properties of the acid-labile subunit from human serum. J Biol Chem 264: 11843–11838 - PubMed
-
- Brugts M.P., van den Beld A.W., Hofland L.J., van der Wansem K., van Koetsveld P.M., Frystyk J., et al. (2008) Low circulating insulin-like growth factor I bioactivity in elderly men is associated with increased mortality. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93: 2515–2522, DOI: 10.1210/jc.2007-163310.1210/jc.2007-1633 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buck E., Eyzaguirre A., Rosenfeld-Franklin M., Thomson S., Mulvihill M., Barr S., et al. (2008) Feedback mechanisms promote cooperativity for small molecule inhibitors of epidermal and insulin-like growth factor receptors. Cancer Res 68: 8322–8332, DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-672010.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6720 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

