Zinc sequestration by the neutrophil protein calprotectin enhances Salmonella growth in the inflamed gut
- PMID: 22423963
- PMCID: PMC3308348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.01.017
Zinc sequestration by the neutrophil protein calprotectin enhances Salmonella growth in the inflamed gut
Abstract
Neutrophils are innate immune cells that counter pathogens by many mechanisms, including release of antimicrobial proteins such as calprotectin to inhibit bacterial growth. Calprotectin sequesters essential micronutrient metals such as zinc, thereby limiting their availability to microbes, a process termed nutritional immunity. We find that while calprotectin is induced by neutrophils during infection with the gut pathogen Salmonella Typhimurium, calprotectin-mediated metal sequestration does not inhibit S. Typhimurium proliferation. Remarkably, S. Typhimurium overcomes calprotectin-mediated zinc chelation by expressing a high affinity zinc transporter (ZnuABC). A S. Typhimurium znuA mutant impaired for growth in the inflamed gut was rescued in the absence of calprotectin. ZnuABC was also required to promote the growth of S. Typhimurium over that of competing commensal bacteria. Thus, our findings indicate that Salmonella thrives in the inflamed gut by overcoming the zinc sequestration of calprotectin and highlight the importance of zinc acquisition in bacterial intestinal colonization.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

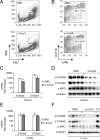
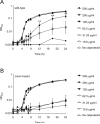
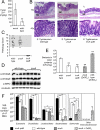
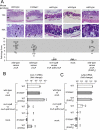
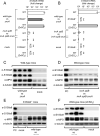
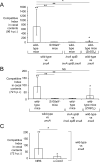
Comment in
-
Bacterial pathogenesis: A competitive edge for Salmonella.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Apr 11;10(5):309. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2784. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22491363 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ammendola S, Pasquali P, Pistoia C, Petrucci P, Petrarca P, Rotilio G, Battistoni A. High-affinity Zn2+ uptake system ZnuABC is required for bacterial zinc homeostasis in intracellular environments and contributes to the virulence of Salmonella enterica. Infection and immunity. 2007;75:5867–5876. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barthel M, Hapfelmeier S, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Kremer M, Rohde M, Hogardt M, Pfeffer K, Russmann H, Hardt WD. Pretreatment of mice with streptomycin provides a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium colitis model that allows analysis of both pathogen and host. Infection and immunity. 2003;71:2839–2858. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI083619/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI060573/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI083663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI073843/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI083663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI091771/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062112/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA062203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM62112-08S1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS041249/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI60573/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS041249/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI083619/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI073843/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI091771/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

