Risk factors for morbidity and death in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis: a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of CT diagnosed bronchiectatic patients
- PMID: 22423975
- PMCID: PMC3379934
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-21
Risk factors for morbidity and death in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis: a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of CT diagnosed bronchiectatic patients
Abstract
Introduction: There is a relative lack of information about the death rate and morbidity of non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis and most studies are limited due to referral bias. We wanted to assess death rate and morbidity in those patients at our hospital.
Methods: Adult patients seen at our department between June 2006 and November 2009 were recruited if the key string "bronchiect-" was mentioned in electronic clinical records and if chest CT imaging was available. Clinical records of all patients with confirmed radiologic diagnosis of bronchiectasis were reviewed and clinical characteristics were analyzed.
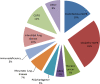
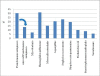
Results: 539 patients with a radiographic diagnosis of non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis were identified in a retrospective cross-sectional analysis giving a prevalence of 2.6% in our hospital population. A wide range of etiologies was found with idiopathic bronchiectasis in 26%. In the 41 months interval, 57 patients (10.6%) died. We found a median exacerbation rate of 1.94 per year. Bacterial colonization status was associated with more deaths, exacerbation rate, symptoms and reduced pulmonary function. Pulmonary hypertension was found in 48% of our patients.
Conclusions: We evaluated a large non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis population, and provided new epidemiological data on associations between clinical characteristics and deaths and morbidity in these patients.
Figures

References
-
- Shah RM, Sexauer W, Ostrum BJ, Fiel SB, Friedman AC. High-resolution CT in the acute exacerbation of cystic fibrosis: evaluation of acute findings, reversibility of those findings, and clinical correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997;169:375–380. - PubMed
-
- Pasteur MC, Helliwell SM, Houghton SJ, Webb SC, Foweraker JE, Coulden RA, Flower CD, Bilton D, Keogan MT. An investigation into causative factors in patients with bronchiectasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:1277–1284. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

