Burden of cancer in Malawi; common types, incidence and trends: national population-based cancer registry
- PMID: 22424105
- PMCID: PMC3327635
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-149
Burden of cancer in Malawi; common types, incidence and trends: national population-based cancer registry
Abstract
Background: Cancer is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide with a majority of cases and deaths occurring in developing countries. While cancer of the lung, breast, colorectum, stomach and prostate are the most common types of cancer globally, in east and southern Africa these are less common and comprehensive data to inform policies are lacking.
Methods: Nationwide cancer registry was conducted between September and October 2010 in Malawi. New cancer cases registered from 2007 to 2010 were identified from hospital and clinic registers of 81 out of 84 health facilities providing cancer diagnosis, treatment or palliative care services. Demographic and cancer data were extracted from registers and case notes using a standard form.
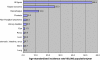
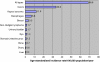
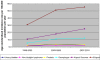
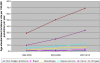
Results: A total of 18,946 new cases of cancer were registered in Malawi from 2007-2010. Of these 55.9% were females, 7.2% were children aged less than 15 years, 76.5% were adults aged 15-59 years and 16.4% were elderly aged 60 years or more. Only 17.9% of the cases had histologically verified diagnosis, 33.2% were diagnosed clinically and 49.6% based on clinical and some investigations. Amongst females, cancer of the cervix was the commonest accounting for 45.4% of all cases followed by Kaposi sarcoma (21.1%), cancer of the oesophagus (8.2%), breast (4.6%) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (4.1%). In males, Kaposi sarcoma was the most frequent (50.7%) then cancer of oesophagus (16.9%), non-Hodgkin lymphoma (7.8), prostate (4.0%) and urinary bladder (3.7%). Age-standardised incidence rate per 100,000 population for all types of cancer in males increased from 31 in 1999-2002 to 56 in 2007-2010. In females it increased from 29 to 69. Kaposi sarcoma and cancer of the oesophagus, cervical cancer and Kaposi sarcoma were the main causes for the increased incidence in males and females respectively. It was estimated that, annually at least 8,151 new cases of cancer (all types) occur in Malawi.
Conclusions: This study provided data on common types and trends of cancer that could be used to focus prevention, treatment and control interventions in the context of limited resources. The problem of under-reporting and misdiagnosis of cancer cases has been highlighted.
© 2010 Msyamboza et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Globocan 2008 Report. IARC: Lyon; 2008. 2008.
-
- World Health Organization. Cancer fact sheet no. 297. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011.
-
- Parkin DM, Ferlay J, Hamdi-Cherif M, Sitas F, Thomas J, Wabinga H, Whelan S L. Cancer in Africa: Epidemiology and Prevention. Lyon, France: lnternational Agency for Research on Cancer; 2003.
-
- Sitas F, Parkin M, Chirenje Z, Stein L, Mqoqi N, Wabinga H. Disease and Mortality in Sub-Saharan Africa. 2. Washington (DC): World Bank; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical