MicroRNAs in stress signaling and human disease
- PMID: 22424228
- PMCID: PMC3308137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.005
MicroRNAs in stress signaling and human disease
Abstract
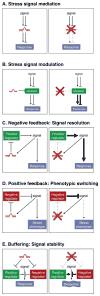
Disease is often the result of an aberrant or inadequate response to physiologic and pathophysiologic stress. Studies over the last 10 years have uncovered a recurring paradigm in which microRNAs (miRNAs) regulate cellular behavior under these conditions, suggesting an especially significant role for these small RNAs in pathologic settings. Here, we review emerging principles of miRNA regulation of stress signaling pathways and apply these concepts to our understanding of the roles of miRNAs in disease. These discussions further highlight the unique challenges and opportunities associated with the mechanistic dissection of miRNA functions and the development of miRNA-based therapeutics.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abelson JF, Kwan KY, O’Roak BJ, Baek DY, Stillman AA, Morgan TM, Mathews CA, Pauls DL, Rasin MR, Gunel M, et al. Sequence variants in SLITRK1 are associated with Tourette’s syndrome. Science. 2005;310:317–320. - PubMed
-
- Alexiou P, Maragkakis M, Papadopoulos GL, Reczko M, Hatzigeorgiou AG. Lost in translation: an assessment and perspective for computational microRNA target identification. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:3049–3055. - PubMed
-
- Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, Ruf IK, Pritchard CC, Gibson DF, Mitchell PS, Bennett CF, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Stirewalt DL, et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:5003–5008. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

