Radiation treatment inhibits monocyte entry into the optic nerve head and prevents neuronal damage in a mouse model of glaucoma
- PMID: 22426214
- PMCID: PMC3314470
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI61135
Radiation treatment inhibits monocyte entry into the optic nerve head and prevents neuronal damage in a mouse model of glaucoma
Abstract
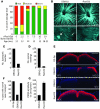
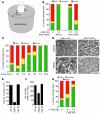
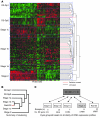
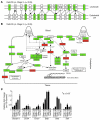
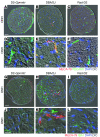
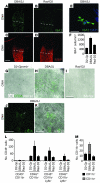
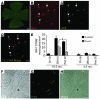
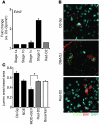
Glaucoma is a common ocular disorder that is a leading cause of blindness worldwide. It is characterized by the dysfunction and loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). Although many studies have implicated various molecules in glaucoma, no mechanism has been shown to be responsible for the earliest detectable damage to RGCs and their axons in the optic nerve. Here, we show that the leukocyte transendothelial migration pathway is activated in the optic nerve head at the earliest stages of disease in an inherited mouse model of glaucoma. This resulted in proinflammatory monocytes entering the optic nerve prior to detectable neuronal damage. A 1-time x-ray treatment prevented monocyte entry and subsequent glaucomatous damage. A single x-ray treatment of an individual eye in young mice provided that eye with long-term protection from glaucoma but had no effect on the contralateral eye. Localized radiation treatment prevented detectable neuronal damage and dysfunction in treated eyes, despite the continued presence of other glaucomatous stresses and signaling pathways. Injection of endothelin-2, a damaging mediator produced by the monocytes, into irradiated eyes, combined with the other glaucomatous stresses, restored neural damage with a topography characteristic of glaucoma. Together, these data support a model of glaucomatous damage involving monocyte entry into the optic nerve.
Figures
References
-
- May CA, Lütjen-Drecoll E. Morphology of the murine optic nerve. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43(7):2206–2212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R29 EY011721/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY018606/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018825/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018606/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY019077/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY021525/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY011721/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY011721/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY014801/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- T32 NS051112/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS51112-05/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY017673/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

