Signal quality assessment of retinal optical coherence tomography images
- PMID: 22427567
- PMCID: PMC3995569
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.11-8755
Signal quality assessment of retinal optical coherence tomography images
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this article was to assess signal quality of retinal optical coherence tomography (OCT) images from multiple devices using subjective and quantitative measurements.
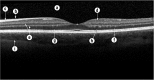
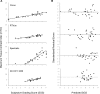
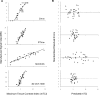
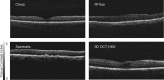
Methods: A total of 120 multiframe OCT images from 4 spectral domain OCT devices (Cirrus, RTVue, Spectralis, and 3D OCT-1000) were evaluated subjectively by trained graders, and measured quantitatively using a derived parameter, maximum tissue contrast index (mTCI). An intensity histogram decomposition model was proposed to separate the foreground and background information of OCT images and to calculate the mTCI. The mTCI results were compared with the manufacturer signal index (MSI) provided by the respective devices, and to the subjective grading scores (SGS).
Results: Statistically significant correlations were observed between the paired methods (i.e., SGS and MSI, SGS and mTCI, and mTCI and MSI). Fisher's Z transformation indicated the Pearson correlation coefficient ρ ≥ 0.8 for all devices. Using the Deming regression, correlation parameters between the paired methods were established. This allowed conversion from the proprietary MSI values to SGS and mTCI that are universally applied to each device.
Conclusions: The study suggests signal quality of retinal OCT images can be evaluated subjectively and objectively, independent of the devices. Together with the proposed histogram decomposition model, mTCI may be used as a standardization metric for OCT signal quality that would affect measurements.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

References
-
- Fujimoto J, Bouma B, Tearney G, et al. New technology for high speed and high resolution optical coherence tomography. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;838:95–107. - PubMed
-
- van Velthoven ME, Faber DJ, Verbraak FD, van Leeuwen TG, de Smet MD. Recent developments in optical coherence tomography for imaging the retina. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2007;26:57–77. - PubMed
-
- Giani A, Cigada M, Choudhry N, et al. Reproducibility of retinal thickness measurements on normal and pathologic eyes by different optical coherence tomography instruments. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010;150:815–824. - PubMed
-
- Geitzenauer W, Kiss C, Durbin M, et al. Comparing retinal thickness measurements from cirrus spectral domain-and stratus time domain-optical coherence tomography. Retina. 2010;30:596–606. - PubMed
-
- Cheung CYL, Leung CKS, Lin D, Pang CP, Lam DSC. Relationship between retinal nerve fiber layer measurement and signal strength in optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:1347–1351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

