Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease
- PMID: 22428854
- PMCID: PMC3410706
- DOI: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v32.i1.30
Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease
Abstract
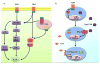
Interleukin 10 (IL-10) is a cytokine with potent anti-inflammatory properties that plays a central role in limiting host immune response to pathogens, thereby preventing damage to the host and maintaining normal tissue homeostasis. Dysregulation of IL-10 is associated with enhanced immunopathology in response to infection as well as increased risk for development of many autoimmune diseases. Thus a fundamental understanding of IL-10 gene expression is critical for our comprehension of disease progression and resolution of host inflammatory response. In this review, we discuss modes of regulation of IL-10 gene expression in immune effector cell types, including signal transduction, epigenetics, promoter architecture, and post-transcriptional regulation, and how aberrant regulation contributes to immunopathology and disease progression.
Figures
References
-
- Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O’Garra A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:683–765. - PubMed
-
- Sabat R, Grütz G, Warszawska K, Kirsch S, Witte E, Wolk K, Geginet J. Biology of interleukin-10. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010 Oct;21(5):331–44. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn R, Lohler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, Muller W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell. 1993;75:263–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

