Sustained rheumatoid arthritis remission is uncommon in clinical practice
- PMID: 22429277
- PMCID: PMC3446437
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3785
Sustained rheumatoid arthritis remission is uncommon in clinical practice
Abstract
Introduction: Remission is an important goal of therapy in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but data on duration of remission are lacking. Our objective was to describe the duration of remission in RA, assessed by different criteria.
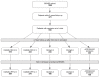
Methods: We evaluated patients from the Brigham and Women's Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study (BRASS) not in remission at baseline with at least 2 years of follow-up. Remission was assessed according to the Disease Activity Score 28-C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP4), Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI), and Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) scores, and the recently proposed American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/European League against Rheumatism (EULAR) criteria for remission. Analyses were performed by using Kaplan-Meier survival curves.
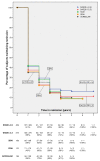
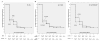
Results: We identified 871 subjects with ≥ 2 years of follow-up. Of these subjects, 394 were in remission at one or more time-points and not in remission at baseline, according to at least one of the following criteria: DAS28-CRP < 2.6 (n = 309), DAS28-CRP < 2.3 (n = 275), SDAI (n = 168), CDAI (n = 170), and 2010 ACR/EULAR (n = 158). The median age for the 394 subjects at entrance to BRASS was 56 years; median disease duration was 8 years; 81% were female patients; and 72% were seropositive. Survival analysis performed separately for each remission criterion demonstrated that < 50% of subjects remained in remission 1 year later. Median remission survival time was 1 year. Kaplan-Meier curves of the various remission criteria did not significantly differ (P = 0.29 according to the log-rank test).
Conclusions: This study shows that in clinical practice, a minority of RA patients are in sustained remission.
Figures
Comment in
-
Nothing lasts forever - a critical look at sustained remission.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 May 9;14(3):116. doi: 10.1186/ar3795. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22577881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewe R, Breedveld FC, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C, Gorter S, Knevel R, Nam J, Schoels M, Aletaha D, Buch M, Gossec L, Huizinga T, Bijlsma JW, Burmester G, Combe B, Cutolo M, Gabay C, Gomez-Reino J, Kouloumas M, Kvien TK, Martin-Mola E, McInnes I, Pavelka K, van Riel P, Scholte M, Scott DL, Sokka T, Valesini G. et al.EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:964–975. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.126532. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

