Biological role of connexin intercellular channels and hemichannels
- PMID: 22430362
- PMCID: PMC3376239
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.03.008
Biological role of connexin intercellular channels and hemichannels
Abstract
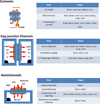
Gap junctions (GJ) and hemichannels (HC) formed from the protein subunits called connexins are transmembrane conduits for the exchange of small molecules and ions. Connexins and another group of HC-forming proteins, pannexins comprise the two families of transmembrane proteins ubiquitously distributed in vertebrates. Most cell types express more than one connexin or pannexin. While connexin expression and channel activity may vary as a function of physiological and pathological states of the cell and tissue, only a few studies suggest the involvement of pannexin HC in acquired pathological conditions. Importantly, genetic mutations in connexin appear to interfere with GJ and HC function which results in several diseases. Thus connexins could serve as potential drug target for therapeutic intervention. Growing evidence suggests that diseases resulting from HC dysfunction might open a new direction for development of specific HC reagents. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the current studies of GJ and HC formed by connexins and pannexins in various tissue and organ systems including heart, central nervous system, kidney, mammary glands, ovary, testis, lens, retina, inner ear, bone, cartilage, lung and liver. In addition, present knowledge of the role of GJ and HC in cell cycle progression, carcinogenesis and stem cell development is also discussed.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

