Pharmacokinetics of ferroquine, a novel 4-aminoquinoline, in asymptomatic carriers of Plasmodium falciparum infections
- PMID: 22430976
- PMCID: PMC3370764
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.05359-11
Pharmacokinetics of ferroquine, a novel 4-aminoquinoline, in asymptomatic carriers of Plasmodium falciparum infections
Abstract
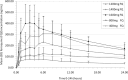
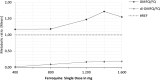
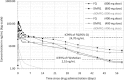
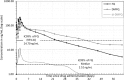
Ferroquine (SSR97193), a ferrocene-quinoline conjugate, is a promising novel antimalarial currently undergoing clinical evaluation. This study characterizes its pharmacokinetic properties. Young male African volunteers with asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum infection were administered a single oral dose (n = 40) or a repeated oral dose (n = 26) given over 3 days of ferroquine in two dose-escalation, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. In addition, a food interaction study was performed in a subsample of participants (n = 16). The studies were carried out in Lambaréné, Gabon. After single-dose administration of ferroquine, dose linearity was demonstrated in a dose range of 400 to 1,200 mg for maximum mean blood concentrations ([C(max)] 82 to 270 ng/ml) and in a dose range of 400 to 1,600 mg for overall exposure to ferroquine (area under the concentration-time curve [AUC], 13,100 to 49,200 ng · h/ml). Overall mean estimate for blood apparent terminal half-life of ferroquine was 16 days and 31 days for its active and major metabolite desmethylferroquine (SSR97213). In the 3-day repeated-dose study, C(max) and overall cumulated exposure to ferroquine (AUC(cum)) increased in proportion with the dose from day 1 to day 3 between 400 and 800 mg. No major food effect on ferroquine pharmacokinetics was observed after single administration of 100 mg of ferroquine except for a slight delay of time to maximum blood concentration (t(max)) by approximately 3 h. The pharmacokinetics of ferroquine and its active main metabolite are characterized by sustained levels in blood, and the properties of ferroquine as a partner drug in antimalarial combination therapy should be evaluated.
Figures


References
-
- Atteke C, et al. 2003. In vitro susceptibility to a new antimalarial organometallic analogue, ferroquine, of Plasmodium falciparum isolates from the Haut-Ogooue region of Gabon. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 51:1021–1024 - PubMed
-
- Baird JK. 2005. Effectiveness of antimalarial drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 352:1565–1577 - PubMed
-
- Biot C, Glorian G, Maciejewski LA, Brocard JS. 1997. Synthesis and antimalarial activity in vitro and in vivo of a new ferrocene-chloroquine analogue. J. Med. Chem. 40:3715–3718 - PubMed
-
- Biot C, et al. 1999. Synthesis and antimalarial activity in vitro of potential metabolites of ferrochloroquine and related compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 7:2843–2847 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

