Synaptic underpinnings of altered hippocampal function in glutaminase-deficient mice during maturation
- PMID: 22431402
- PMCID: PMC3531559
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.22014
Synaptic underpinnings of altered hippocampal function in glutaminase-deficient mice during maturation
Abstract
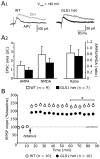
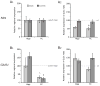
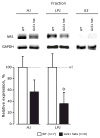
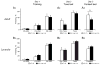
Glutaminase-deficient mice (GLS1 hets), with reduced glutamate recycling, have a focal reduction in hippocampal activity, mainly in CA1, and manifest behavioral and neurochemical phenotypes suggestive of schizophrenia resilience. To address the basis for the hippocampal hypoactivity, we examined synaptic plastic mechanisms and glutamate receptor expression. Although baseline synaptic strength was unaffected in Schaffer collateral inputs to CA1, we found that long-term potentiation was attenuated. In wild-type (WT) mice, GLS1 gene expression was highest in the hippocampus and cortex, where it was reduced by about 50% in GLS1 hets. In other brain regions with lower WT GLS1 gene expression, there were no genotypic reductions. In adult GLS1 hets, NMDA receptor NR1 subunit gene expression was reduced, but not AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit gene expression. In contrast, juvenile GLS1 hets showed no reductions in NR1 gene expression. In concert with this, adult GLS1 hets showed a deficit in hippocampal-dependent contextual fear conditioning, whereas juvenile GLS1 hets did not. These alterations in glutamatergic synaptic function may partly explain the hippocampal hypoactivity seen in the GLS1 hets. The maturity-onset reduction in NR1 gene expression and in contextual learning supports the premise that glutaminase inhibition in adulthood should prove therapeutic in schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
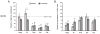
References
-
- Abramoff M, Magalhaes P, Ram S. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004;11(7):36–42.
-
- Anand A, Charney DS, Oren DA, Berman RM, Hu XS, Cappiello A, Krystal JH. Attenuation of the neuropsychiatric effects of ketamine with lamotrigine: support for hyperglutamatergic effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57(3):270–6. - PubMed
-
- Balschun D, Moechars D, Callaerts-Vegh Z, Vermaercke B, Van Acker N, Andries L, D’Hooge R. Vesicular glutamate transporter VGLUT1 has a role in hippocampal long-term potentiation and spatial reversal learning. Cereb Cortex. 2009;20(3):684–693. - PubMed
-
- Barak S, Weiner I. The M1/M4 preferring agonist xanomeline reverses amphetamine-, MK801- and scopolamine-induced abnormalities of latent inhibition: putative efficacy against positive, negative and cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011;14(9):1233–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

