Reversibility of fenofibrate therapy-induced renal function impairment in ACCORD type 2 diabetic participants
- PMID: 22432114
- PMCID: PMC3329840
- DOI: 10.2337/dc11-1811
Reversibility of fenofibrate therapy-induced renal function impairment in ACCORD type 2 diabetic participants
Abstract
Objective: To assess the reversibility of the elevation of serum creatinine levels in patients with diabetes after 5 years of continuous on-trial fenofibrate therapy.
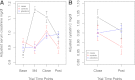
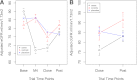
Research design and methods: An on-drug/off-drug ancillary study to the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) Lipid Trial to investigate posttrial changes in serum creatinine and cystatin C. Eligible participants were recruited into a prospective, nested, three-group study based on retrospective on-trial serum creatinine levels: fenofibrate case subjects (n = 321, ≥ 20% increase after 3 months of therapy); fenofibrate control subjects (n = 175, ≤ 2% increase); and placebo control subjects (n = 565). Serum creatinine and cystatin C were measured at trial end and 6-8 weeks after discontinuation of trial therapy. RESULTS At trial end, case subjects had the highest adjusted serum creatinine (± SE) mg/dL (1.11 ± 0.02) and the lowest adjusted estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (± SE) mL/min/1.73 m(2) (68.4 ± 1.0) versus control subjects (1.01 ± 0.02; 74.8 ± 1.3) and placebo subjects (0.98 ± 0.01; 77.8 ± 0.7). After 51 days off-drug, serum creatinine in case subjects was still higher (0.97 ± 0.02) and eGFR still lower (77.8 ± 1.0) than control subjects (0.90 ± 0.02; 81.8 ± 1.3) but not different from placebo subjects (0.99 ± 0.01; 76.6 ± 0.7). Changes in serum cystatin C recapitulated the serum creatinine changes.
Conclusions: Participants with significant initial on-trial increases in serum creatinine (≥ 20%) returned to the same level of renal function as participants receiving placebo while participants who had ≤ 2% increase in serum creatinine had net preservation of renal function compared with the same unselected placebo reference group. The fenofibrate-associated on-trial increases in serum creatinine were reversible, and the reversal was complete after 51 days off-drug. The similarity of the cystatin C results suggests that the mechanism of this change is not specific for serum creatinine.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00000620.
Figures
References
-
- Broeders N, Knoop C, Antoine M, Tielemans C, Abramowicz D. Fibrate-induced increase in blood urea and creatinine: is gemfibrozil the only innocuous agent? Nephrol Dial Transplant 2000;15:1993–1999 - PubMed
-
- Lipscombe J, Lewis GF, Cattran D, Bargman JM. Deterioration in renal function associated with fibrate therapy. Clin Nephrol 2001;55:39–44 - PubMed
-
- Boissonnat P, Salen P, Guidollet J, et al. The long-term effects of the lipid-lowering agent fenofibrate in hyperlipidemic heart transplant recipients. Transplantation 1994;58:245–247 - PubMed
-
- Rössner S, Orö L. Fenofibrate therapy of hyperlipoproteinaemia. A dose-response study and a comparison with clofibrate. Atherosclerosis 1981;38:273–282 - PubMed
-
- Ansquer JC, Foucher C, Rattier S, Taskinen MR, Steiner G, DAIS Investigators Fenofibrate reduces progression to microalbuminuria over 3 years in a placebo-controlled study in type 2 diabetes: results from the Diabetes Atherosclerosis Intervention Study (DAIS). Am J Kidney Dis 2005;45:485–493 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095179/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095184/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95180/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095178/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95184/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- IAA-Y1-HC-1010/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095182/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95183/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95178/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95179/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95181/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- IAA-Y1-HC-9035/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095180/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Y01 HC001010/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Y01 HC009035/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095181/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95182/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095183/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

