Donor lung derived myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells differentially regulate T cell proliferation and cytokine production
- PMID: 22433165
- PMCID: PMC3352265
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-25
Donor lung derived myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells differentially regulate T cell proliferation and cytokine production
Abstract
Background: Direct allorecognition, i.e., donor lung-derived dendritic cells (DCs) stimulating recipient-derived T lymphocytes, is believed to be the key mechanism of lung allograft rejection. Myeloid (cDCs) and plasmacytoid (pDCs) are believed to have differential effects on T cell activation. However, the roles of each DC type on T cell activation and rejection pathology post lung transplantation are unknown.
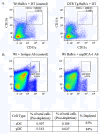
Methods: Using transgenic mice and antibody depletion techniques, either or both cell types were depleted in lungs of donor BALB/c mice (H-2(d)) prior to transplanting into C57BL/6 mice (H-2(b)), followed by an assessment of rejection pathology, and pDC or cDC-induced proliferation and cytokine production in C57BL/6-derived mediastinal lymph node T cells (CD3+).
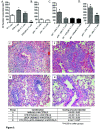
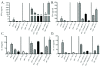
Results: Depleting either DC type had modest effect on rejection pathology and T cell proliferation. In contrast, T cells from mice that received grafts depleted of both DCs did not proliferate and this was associated with significantly reduced acute rejection scores compared to all other groups. cDCs were potent inducers of IFNγ, whereas both cDCs and pDCs induced IL-10. Both cell types had variable effects on IL-17A production.
Conclusion: Collectively, the data show that direct allorecognition by donor lung pDCs and cDCs have differential effects on T cell proliferation and cytokine production. Depletion of both donor lung cDC and pDC could prevent the severity of acute rejection episodes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Depletion of donor dendritic cells ameliorates immunogenicity of both skin and hind limb transplants.Front Immunol. 2024 May 10;15:1395945. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395945. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38799435 Free PMC article.
-
Role of passenger leukocytes in allograft rejection: effect of depletion of donor alveolar macrophages on the local production of TNF-alpha, T helper 1/T helper 2 cytokines, IgG subclasses, and pathology in a rat model of lung transplantation.J Immunol. 1997 Oct 15;159(8):4084-93. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9378999
-
Instillation of allogeneic lung macrophages and dendritic cells cause differential effects on local IFN-gamma production, lymphocytic bronchitis, and vasculitis in recipient murine lungs.J Leukoc Biol. 1998 Nov;64(5):578-86. doi: 10.1002/jlb.64.5.578. J Leukoc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9823761
-
Role of dendritic cell synthesis of complement in the allospecific T cell response.Mol Immunol. 2007 Jan;44(1-3):57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.06.012. Epub 2006 Jul 25. Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 16870256 Review.
-
Effects of gene induction and cytokine production in donor care.Prog Transplant. 2003 Mar;13(1):9-14; quiz 15-6. doi: 10.1177/152692480301300103. Prog Transplant. 2003. PMID: 12688643 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: no longer an enigma and now key to transplant tolerance?Am J Transplant. 2013 May;13(5):1125-33. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12229. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Am J Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23617754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Daud SA, Yusen RD, Meyers BF, Chakinala MM, Walter MJ, Aloush AA, Patterson GA, Trulock EP, Hachem RR. Impact of immediate primary lung allograft dysfunction on bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2007;175(5):507–513. - PubMed
-
- Huang HJ, Yusen RD, Meyers BF, Walter MJ, Mohanakumar T, Patterson GA, Trulock EP, Hachem RR. Late Primary Graft Dysfunction After Lung Transplantation and Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome. American Journal of Transplantation. 2008;8(11):2454–2462. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02389.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gelman AE, Li W, Richardson SB, Zinselmeyer BH, Lai J, Okazaki M, Kornfeld CG, Kreisel FH, Sugimoto S, Tietjens JR. et al.Cutting Edge: Acute Lung Allograft Rejection Is Independent of Secondary Lymphoid Organs. The Journal of Immunology. 2009;182(7):3969–3973. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803514. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mazariegos GV, Zahorchak AF, Reyes J, Chapman H, Zeevi A, Thomson AW. Dendritic Cell Subset Ratio in Tolerant, Weaning and Non-Tolerant Liver Recipients Is Not Affected by Extent of Immunosuppression. American Journal of Transplantation. 2005;5(2):314–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2004.00672.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

