Effect of daily aciclovir on HIV disease progression in individuals in Rakai, Uganda, co-infected with HIV-1 and herpes simplex virus type 2: a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 22433279
- PMCID: PMC3420068
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70037-3
Effect of daily aciclovir on HIV disease progression in individuals in Rakai, Uganda, co-infected with HIV-1 and herpes simplex virus type 2: a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Daily suppression of herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) reduces plasma HIV-1 concentrations and modestly delayed HIV-1 disease progression in one clinical trial. We investigated the effect of daily suppressive aciclovir on HIV-1 disease progression in Rakai, Uganda.
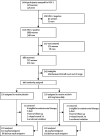
Methods: We did a single site, parallel, randomised, controlled trial of HIV-1, HSV-2 dually infected adults with CD4 cell counts of 300-400 cells per μL. We excluded individuals who had an AIDS-defining illness or active genital ulcer disease, and those that were taking antiretroviral therapy. Participants were randomly assigned (1:1) with computer-generated random numbers in blocks of four to receive either aciclovir 400 mg orally twice daily or placebo; participants were followed up for 24 months. All study staff and participants were masked to treatment, except for the two statisticians. The primary outcome was CD4 cell count less than 250 cells per μL or initiation of antiretroviral therapy for WHO stage 4 disease. Our intention-to-treat analysis used Cox proportional hazards models, adjusting for baseline log(10) viral load, CD4 cell count, sex, and age to assess the risk of disease progression. We also investigated the effect of suppressive HSV-2 treatment stratified by baseline HIV viral load with a Cox proportional hazards model. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT00405821.
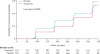
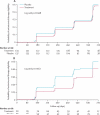
Findings: 440 participants were randomly assigned, 220 to each group. 110 participants in the placebo group and 95 participants in the treatment group reached the primary endpoint (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 0·75, 95% CI 0·58-0·99; p=0·040). 24 participants in the placebo group and 22 in the treatment group were censored, but all contributed data for the final analysis. In a subanalysis stratified by baseline HIV viral load, participants with a baseline viral load of 50,000 copies mL or more in the treatment group had a reduced HIV disease progression compared with those in the placebo group (0·62, 0·43-0·96; p=0·03). No significant difference in HIV disease progression existed between participants in the treatment group and those in the placebo group who had baseline HIV viral loads of less than 50,000 copies per mL (0·90, 0·54-1·5; p=0·688). No safety issues related to aciclovir treatment were identified.
Interpretation: Aciclovir reduces the rate of disease progression, with the greatest effect in individuals with a high baseline viral load. Suppressive aciclovir might be warranted for individuals dually infected with HSV-2 and HIV-1 with viral loads of 50,000 copies per mL or more before initiation of antiretroviral treatment.
Funding: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Cancer Institute (National Institutes of Health, USA).
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Aciclovir for dual infection with HIV and HSV.Lancet Infect Dis. 2012 Jun;12(6):424-5. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70050-6. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22433278 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Daily acyclovir for HIV-1 disease progression in people dually infected with HIV-1 and herpes simplex virus type 2: a randomised placebo-controlled trial.Lancet. 2010 Mar 6;375(9717):824-33. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)62038-9. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Lancet. 2010. PMID: 20153888 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of aciclovir on HIV-1 acquisition in herpes simplex virus 2 seropositive women and men who have sex with men: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet. 2008 Jun 21;371(9630):2109-19. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60920-4. Lancet. 2008. PMID: 18572080 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of aciclovir on genital and plasma HIV-1 RNA in HSV-2/HIV-1 co-infected women: a randomized placebo-controlled trial in South Africa.AIDS. 2009 Feb 20;23(4):461-9. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32831db217. AIDS. 2009. PMID: 19155993 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Valaciclovir: a review of its long term utility in the management of genital herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus infections.Drugs. 2000 Apr;59(4):839-63. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200059040-00013. Drugs. 2000. PMID: 10804039 Review.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Frequent detection of HPV before and after initiation of antiretroviral therapy among HIV/HSV-2 co-infected women in Uganda.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055383. Epub 2013 Jan 29. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383171 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of valacyclovir on markers of disease progression in postpartum women co-infected with HIV-1 and herpes simplex virus-2.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038622. Epub 2012 Jun 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22701683 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 2 in sub-Saharan Africa and the potential impact of helminth immune modulation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Dec 4;14:1471411. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1471411. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39698320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaginal Cytomegalovirus Shedding Before and After Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy in Rakai, Uganda.J Infect Dis. 2015 Sep 15;212(6):899-903. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv135. Epub 2015 Mar 5. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25743428 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
HIV infection and immune activation: the role of coinfections.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2016 Mar;11(2):191-200. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000241. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2016. PMID: 26720550 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moriuchi M, Moriuchi H, Williams R, Straus SE. Herpes simplex virus infection induces replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Virology. 2000 Dec 20;278(2):534–40. - PubMed
-
- Mbopi-Keou FX, Gresenguet G, Mayaud P, Weiss HA, Gopal R, Matta M, et al. Interactions between herpes simplex virus type 2 and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in African women: opportunities for intervention. J Infect Dis. 2000 Oct;182(4):1090–6. - PubMed
-
- Serwadda D, Gray RH, Sewankambo NK, Wabwire-Mangen F, Chen MZ, Quinn TC, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus acquisition associated with genital ulcer disease and herpes simplex virus type 2 infection: a nested case-control study in Rakai, Uganda. J Infect Dis. 2003 Nov 15;188(10):1492–7. - PubMed
-
- McClelland RS, Wang CC, Overbaugh J, Richardson BA, Corey L, Ashley RL, et al. Association between cervical shedding of herpes simplex virus and HIV-1. AIDS. 2002 Dec 6;16(18):2425–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

