Scale matters: the spatial correlation of yeast meiotic DNA breaks with histone H3 trimethylation is driven largely by independent colocalization at promoters
- PMID: 22433953
- PMCID: PMC3341227
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.19733
Scale matters: the spatial correlation of yeast meiotic DNA breaks with histone H3 trimethylation is driven largely by independent colocalization at promoters
Abstract
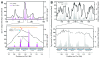
During meiosis in many organisms, homologous chromosomes engage in numerous recombination events initiated by DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) formed by the Spo11 protein. DSBs are distributed nonrandomly, which governs how recombination influences inheritance and genome evolution. The chromosomal features that shape DSB distribution are not well understood. In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, trimethylation of lysine 4 of histone H3 (H3K4me3) has been suggested to play a causal role in targeting Spo11 activity to small regions of preferred DSB formation called hotspots. The link between H3K4me3 and DSBs is supported in part by a genome-wide spatial correlation between the two. However, this correlation has only been evaluated using relatively low-resolution maps of DSBs, H3K4me3 or both. These maps illuminate chromosomal features that influence DSB distributions on a large scale (several kb and greater) but do not adequately resolve features, such as chromatin structure, that act on finer scales (kb and shorter). Using recent nucleotide-resolution maps of DSBs and meiotic chromatin structure, we find that the previously described spatial correlation between H3K4me3 and DSB hotspots is principally attributable to coincident localization of both to gene promoters. Once proximity to the nucleosome-depleted regions in promoters is accounted for, H3K4me3 status has only modest predictive power for determining DSB frequency or location. This analysis provides a cautionary tale about the importance of scale in genome-wide analyses of DSB and recombination patterns.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High-Resolution Global Analysis of the Influences of Bas1 and Ino4 Transcription Factors on Meiotic DNA Break Distributions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2015 Oct;201(2):525-42. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.178293. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 26245832 Free PMC article.
-
The COMPASS subunit Spp1 links histone methylation to initiation of meiotic recombination.Science. 2013 Jan 11;339(6116):215-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1225739. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Science. 2013. PMID: 23160953
-
Meiotic recombination cold spots in chromosomal cohesion sites.Genes Cells. 2014 May;19(5):359-73. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12138. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Genes Cells. 2014. PMID: 24635992
-
Spp1 at the crossroads of H3K4me3 regulation and meiotic recombination.Epigenetics. 2013 Apr;8(4):355-60. doi: 10.4161/epi.24295. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Epigenetics. 2013. PMID: 23511748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating and targeting meiotic double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;557:27-33. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-527-5_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19799174 Review.
Cited by
-
Meiotic DSB patterning: A multifaceted process.Cell Cycle. 2016;15(1):13-21. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1093709. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 26730703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleosomes and DNA methylation shape meiotic DSB frequency in Arabidopsis thaliana transposons and gene regulatory regions.Genome Res. 2018 Apr;28(4):532-546. doi: 10.1101/gr.225599.117. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Genome Res. 2018. PMID: 29530928 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic Recombination: The Essence of Heredity.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Oct 28;7(12):a016618. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016618. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 26511629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic features shaping the landscape of meiotic double-strand-break hotspots in maize.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 14;114(46):12231-12236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1713225114. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29087335 Free PMC article.
-
A Critical Assessment of 60 Years of Maize Intragenic Recombination.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Oct 29;9:1560. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01560. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30420864 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hunter N. Meiotic recombination. In: Aguilera A, Rothstein R, eds. Molecular Genetics of Recombination. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2007:381-442.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
