Serum matrix metalloproteinase 9 and colorectal neoplasia: a community-based evaluation of a potential diagnostic test
- PMID: 22433968
- PMCID: PMC3326675
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.93
Serum matrix metalloproteinase 9 and colorectal neoplasia: a community-based evaluation of a potential diagnostic test
Abstract
Background: A blood test may be a more acceptable routine colorectal cancer (CRC) screening test than faecal occult blood test, flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, and could be safer and cheaper. We evaluated the accuracy of a serum matrix metalloproteinase (MMP9) test for CRC in a non-presenting symptomatic population.
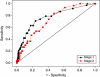
Methods: A cohort, aged 50-69 with lower gastrointestinal symptoms, was identified by community-based survey. Accuracy of serum MMP9 was assessed by comparison with colonoscopy. Logistic regression identified predictors of neoplasia and receiver operating characteristic curve analyses determined the cutoff to maximise the sensitivity.
Results: Data were available for 748 patients. Overall, 46 cases of neoplasia were identified. Univariate analysis demonstrated that demographic characteristics, behavioural factors, clinical symptoms and raised serum MMP9 concentration were all significantly associated with the presence of neoplasia. Our final logistic regression model had a sensitivity of 79% and specificity of 70%.
Conclusion: We demonstrated a significant association between serum MMP9 concentration and the presence of neoplasia. Serum MMP9 levels are raised in those with cancer and high-risk adenomas, although MMP9 estimation is likely to have the greatest predictive utility when used as part of a panel of biomarkers. Further work is required to identify biomarkers that are sufficiently accurate for implementing into routine practice.
Figures
References
-
- Arditi C, Peytremann-Bridevaux I, Burnand B, Eckardt VF, Bytzer P, Agreus L, Dubois RW, Vader JP, Froehlich F, Pittet V, Schussele Filliettaz S, Juillerat P, Gonvers JJ (2009) Appropriateness of colonoscopy in Europe (EPAGE II). Screening for colorectal cancer. Endoscopy 41: 200–208 - PubMed
-
- Atkin WS, Edwards R, Kralj-Hans I, Wooldrage K, Hart AR, Northover JMA, Parkin DM, Wardle J, Duffy SW, Cuzick J (2010) Once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy screening in prevention of colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 375: 1624–1633 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous