The development, past achievements, and future directions of brain PET
- PMID: 22434067
- PMCID: PMC3390812
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.20
The development, past achievements, and future directions of brain PET
Abstract
The early developments of brain positron emission tomography (PET), including the methodological advances that have driven progress, are outlined. The considerable past achievements of brain PET have been summarized in collaboration with contributing experts in specific clinical applications including cerebrovascular disease, movement disorders, dementia, epilepsy, schizophrenia, addiction, depression and anxiety, brain tumors, drug development, and the normal healthy brain. Despite a history of improving methodology and considerable achievements, brain PET research activity is not growing and appears to have diminished. Assessments of the reasons for decline are presented and strategies proposed for reinvigorating brain PET research. Central to this is widening the access to advanced PET procedures through the introduction of lower cost cyclotron and radiochemistry technologies. The support and expertize of the existing major PET centers, and the recruitment of new biologists, bio-mathematicians and chemists to the field would be important for such a revival. New future applications need to be identified, the scope of targets imaged broadened, and the developed expertize exploited in other areas of medical research. Such reinvigoration of the field would enable PET to continue making significant contributions to advance the understanding of the normal and diseased brain and support the development of advanced treatments.
Figures

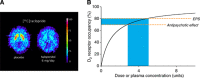
References
-
- Abanades S, Van Der Aart J, Barletta JAR, Marzano C, Searle GE, Salinas CA, Ahmad JJ, Reiley RR, Pampols-Maso S, Zamuner S, Cunningham VJ, Rabiner EA, Laruelle MA, Gunn RN. Prediction of repeat-dose occupancy from single-dose data: characterisation of the relationship between plasma pharmacokinetics and brain target occupancy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011;31:944–952. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ackerman RH, Correia JA, Alpert NM, Baron JC, Gouliamos A, Grotta JC, Brownell GL, Taveras JM. Positron imaging in ischemic stroke disease using compounds labeled with oxygen 15. Initial results of clinicophysiologic correlations. Arch Neurol. 1981;38:537–543. - PubMed
-
- Alavi A, Reivich M. Guest editorial: the conception of FDG-PET imaging. Semin Nucl Med. 2002;32:2–5. - PubMed
-
- Albin RL, Minoshima S, D'Amato CJ, Frey KA, Kuhl DA, Sima AA. Fluoro-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography in diffuse Lewy body disease. Neurology. 1996;47:462–466. - PubMed
-
- Andersson JD, Pierson ME, Finnema SJ, Gulyas B, Heys R, Elmore CS, Farde L, Halldin C. Development of a PET radioligand for the central 5-HT1B receptor: radiosynthesis and characterization in cynomolgus monkeys of eight radiolabeled compounds. Nucl Med Biol. 2011;38:261–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

