Utilization of health information system at district level in jimma zone oromia regional state, South west ethiopia
- PMID: 22435010
- PMCID: PMC3275876
Utilization of health information system at district level in jimma zone oromia regional state, South west ethiopia
Abstract
Introduction: Information systems are increasingly important for measuring and improving the quality and coverage of health services. Reliable and timely health information is vital for operational and strategic decision making that save lives and enhances health. In Ethiopia information quality and use remain weak, particularly at district health offices and primary health care facilities to facilitate decision making. Therefore, the objective of this study is to assess the utilization of health information systems at District level in Jimma Zone, southwest Ethiopia.
Methods: A cross sectional study was conducted in all health institutions by interviewing heads/ units/departments of District Health Office, Health Center and Health Post from January to February, 2009. Quantitative and qualitative data were collected using structured questionnaires, check lists, observation and interview guide by trained data collectors. Data was analyzed using SPSS version 16 and descriptive and logistic regression analysis was carried out.
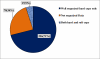
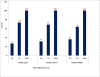
Results: The finding of the study revealed that utilization of health information was 119(32.9%) in all the study units/departments. The major source of data was routine and vertical program report from public institutions. The utilization of information was affected by many factors but from variables studied only documentation of data, catchment population profile charts presentation and quarter plan performance monitoring was found significant at 95 % level of significance.
Conclusion: The study identified that the implementation of health data/information and utilization of health information system was found to be far below the national expectation. Activities are poorly coordinated at the districts and primary health units where data was generated initially. Therefore, in-service training and updating of staff involved in health information system (HIS) at district, strengthening health information system inputs, timely and concrete feedbacks with establishment of functional health management information system (HMIS).
Keywords: Health Management Information System; utilization of health information at Districts.
Figures

References
-
- Chaulagai C, Moyo C, Koot J, Moyo H, Sambakunsi T, Khunga F, et al. Design and implementation of a health management information system in Malawi: issues, innovations and results. 2005. Sep, doi:10.1093/heapol/czi044 Advance access publication 2. - PubMed
-
- Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 2005 Aug;83:561–564. 590–596. Available at: http://www.bulletin@who.int. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), author Primary health care: report of international conference on Primary Health Care. Almata. Geneva; 1978.
-
- Federal Republic of Ethiopia Ministry of Health, author. Management Information System (HMIS) /Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) Strategic Plan for Ethiopian Health Sector HMIS Reform Team. Addis Ababa; 2008. Jan,
-
- AbouZahr C, Boerma T. Health Information Systems: The Foundations of Public Health. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 2005;83(8):578–583. Available at: http://www.bulletin@who.int. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
