Novel polysome messages and changes in translational activity appear after induction of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells
- PMID: 22436005
- PMCID: PMC3347988
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-13-9
Novel polysome messages and changes in translational activity appear after induction of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells
Abstract
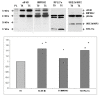
Background: Control of translation allows for rapid adaptation of the cell to stimuli, rather than the slower transcriptional control. We presume that translational control is an essential process in the control of adipogenesis, especially in the first hours after hormonal stimulation. 3T3-L1 preadipocytes were cultured to confluency and adipogenesis was induced by standard protocols using a hormonal cocktail. Cells were harvested before and 6 hours after hormonal induction. mRNAs attached to ribosomes (polysomal mRNAs) were separated from unbound mRNAs by velocity sedimentation. Pools of polysomal and unbound mRNA fractions were analyzed by microarray analysis. Changes in relative abundance in unbound and polysomal mRNA pools were calculated to detect putative changes in translational activity. Changes of expression levels of selected genes were verified by qPCR and Western blotting.
Results: We identified 43 genes that shifted towards the polysomal fraction (up-regulated) and 2 genes that shifted towards free mRNA fraction (down-regulated). Interestingly, we found Ghrelin to be down-regulated. Up-regulated genes comprise factors that are nucleic acid binding (eIF4B, HSF1, IRF6, MYC, POLR2a, RPL18, RPL27a, RPL6, RPL7a, RPS18, RPSa, TSC22d3), form part of ribosomes (RPL18, RPL27a, RPL6, RPL7a, RPS18, RPSa), act on the regulation of translation (eIF4B) or transcription (HSF1, IRF6, MYC, TSC22d3). Others act as chaperones (BAG3, HSPA8, HSP90ab1) or in other metabolic or signals transducing processes.
Conclusions: We conclude that a moderate reorganisation of the functionality of the ribosomal machinery and translational activity are very important steps for growth and gene expression control in the initial phase of adipogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dynamics of mRNA and polysomal abundance in early 3T3-L1 adipogenesis.BMC Genomics. 2014 May 18;15(1):381. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-381. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24886538 Free PMC article.
-
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 is required for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma expression and adipogenesis in cultured 3T3-L1 cells.J Biol Chem. 2008 Feb 1;283(5):2906-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705656200. Epub 2007 Nov 21. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18032385
-
Isolation of translationally controlled mRNAs by differential screening.FASEB J. 2000 Aug;14(11):1641-52. doi: 10.1096/fj.14.11.1641. FASEB J. 2000. PMID: 10928999
-
Genome-wide analysis of mRNA polysomal profiles with spotted DNA microarrays.Methods Enzymol. 2007;431:177-201. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)31010-0. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17923236 Review.
-
Isolation of plant polysomal mRNA by differential centrifugation and ribosome immunopurification methods.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;553:109-26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-563-7_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19588103 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive proteomic biomarkers for inflammatory bowel disease-associated cancer: where are we now in the era of the next generation proteomics?World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 7;20(37):13466-2476. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13466. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25309077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PKM2 uses control of HuR localization to regulate p27 and cell cycle progression in human glioblastoma cells.Int J Cancer. 2016 Jul 1;139(1):99-111. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30041. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26874904 Free PMC article.
-
HSP90AB1: Helping the good and the bad.Gene. 2016 Jan 10;575(2 Pt 1):171-86. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.08.063. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26358502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Looking into laminin receptor: critical discussion regarding the non-integrin 37/67-kDa laminin receptor/RPSA protein.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2016 May;91(2):288-310. doi: 10.1111/brv.12170. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2016. PMID: 25630983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of alternative polyadenylation during adipogenic differentiation: an in silico approach.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 15;8(10):e75578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075578. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24143171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spalding KL, Arner E, Westermark PO, Bernard S, Buchholz BA, Bergmann O, Blomqvist L, Hoffstedt J, Näslund E, Britton T, Concha H, Hassan M, Rydén M, Frisén J, Arner P. Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. Nature. 2008;453:783–787. - PubMed
-
- MacDougald OA, Lane MD. Transcriptional regulation of gene expression during adipocyte differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:345–373. - PubMed
-
- Poulos SP, Dodson MV, Hausman GJ. Cell line models for differentiation: preadipocytes and adipocytes. Exp Biol Med. 2010;235:1185–1193. - PubMed
-
- Burton GR, Guan Y, Nagarajan R, McGehee RE Jr. Microarray analysis of gene expression during early adipocyte differentiation. Gene. 2002;293:21–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

