MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders
- PMID: 22436747
- PMCID: PMC4021399
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3313
MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders
Erratum in
- Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 May;13(5). doi:10.1038/nrm3328
Abstract
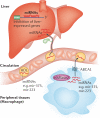
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have recently emerged as key regulators of metabolism. For example, miR-33a and miR-33b have a crucial role in controlling cholesterol and lipid metabolism in concert with their host genes, the sterol-regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) transcription factors. Other metabolic miRNAs, such as miR-103 and miR-107, regulate insulin and glucose homeostasis, whereas miRNAs such as miR-34a are emerging as key regulators of hepatic lipid homeostasis. The discovery of circulating miRNAs has highlighted their potential as both endocrine signalling molecules and disease markers. Dysregulation of miRNAs may contribute to metabolic abnormalities, suggesting that miRNAs may potentially serve as therapeutic targets for ameliorating cardiometabolic disorders.
Figures


References
-
- Lehrke M, Lazar MA. The many faces of PPARgamma. Cell. 2005;123:993–9. - PubMed
-
- Nakae J, Oki M, Cao Y. The FoxO transcription factors and metabolic regulation. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:54–67. - PubMed
-
- Uyeda K, Repa JJ. Carbohydrate response element binding protein, ChREBP, a transcription factor coupling hepatic glucose utilization and lipid synthesis. Cell Metab. 2006;4:107–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

