AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis
- PMID: 22436748
- PMCID: PMC5726489
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3311
AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis
Abstract
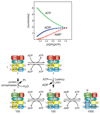
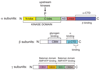
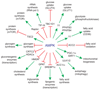
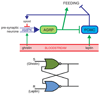
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a crucial cellular energy sensor. Once activated by falling energy status, it promotes ATP production by increasing the activity or expression of proteins involved in catabolism while conserving ATP by switching off biosynthetic pathways. AMPK also regulates metabolic energy balance at the whole-body level. For example, it mediates the effects of agents acting on the hypothalamus that promote feeding and entrains circadian rhythms of metabolism and feeding behaviour. Finally, recent studies reveal that AMPK conserves ATP levels through the regulation of processes other than metabolism, such as the cell cycle and neuronal membrane excitability.
Figures

References
-
- Hardie DG. AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:774–785. - PubMed
-
- Suter M, et al. Dissecting the role of 5'-AMP for allosteric stimulation, activation, and deactivation of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:32207–32216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

