Transcription factor PIF4 controls the thermosensory activation of flowering
- PMID: 22437497
- PMCID: PMC4972390
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10928
Transcription factor PIF4 controls the thermosensory activation of flowering
Abstract
Plant growth and development are strongly affected by small differences in temperature. Current climate change has already altered global plant phenology and distribution, and projected increases in temperature pose a significant challenge to agriculture. Despite the important role of temperature on plant development, the underlying pathways are unknown. It has previously been shown that thermal acceleration of flowering is dependent on the florigen, FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT). How this occurs is, however, not understood, because the major pathway known to upregulate FT, the photoperiod pathway, is not required for thermal acceleration of flowering. Here we demonstrate a direct mechanism by which increasing temperature causes the bHLH transcription factor PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR4 (PIF4) to activate FT. Our findings provide a new understanding of how plants control their timing of reproduction in response to temperature. Flowering time is an important trait in crops as well as affecting the life cycles of pollinator species. A molecular understanding of how temperature affects flowering will be important for mitigating the effects of climate change.
Figures


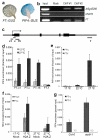
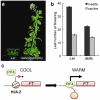
References
-
- Samach A, Wigge PA. Ambient temperature perception in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2005;8:483–486. - PubMed
-
- Fitter AH, Fitter RS. Rapid changes in flowering time in British plants. Science. 2002;296:1689–1691. - PubMed
-
- Battisti DS, Naylor RL. Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat. Science. 2009;323:240–244. - PubMed
-
- Halliday KJ, Salter MG, Thingnaes E, Whitelam GC. Phytochrome control of flowering is temperature sensitive and correlates with expression of the floral integrator FT. Plant J. 2003;33:875–885. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/D0100470/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/000CA346/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- P19972/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/00000610/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/000CA402/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/000C0636/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/00000583/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 243140/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- BB/I019022/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

