The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 22437870
- PMCID: PMC4856023
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc3239
The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
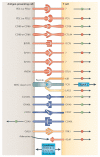
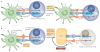
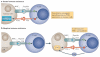
Among the most promising approaches to activating therapeutic antitumour immunity is the blockade of immune checkpoints. Immune checkpoints refer to a plethora of inhibitory pathways hardwired into the immune system that are crucial for maintaining self-tolerance and modulating the duration and amplitude of physiological immune responses in peripheral tissues in order to minimize collateral tissue damage. It is now clear that tumours co-opt certain immune-checkpoint pathways as a major mechanism of immune resistance, particularly against T cells that are specific for tumour antigens. Because many of the immune checkpoints are initiated by ligand-receptor interactions, they can be readily blocked by antibodies or modulated by recombinant forms of ligands or receptors. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA4) antibodies were the first of this class of immunotherapeutics to achieve US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval. Preliminary clinical findings with blockers of additional immune-checkpoint proteins, such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1), indicate broad and diverse opportunities to enhance antitumour immunity with the potential to produce durable clinical responses.
Figures
References
-
- Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. The B7 family revisited. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005;23:515–548. - PubMed
-
-
Zou W, Chen L. Inhibitory B7-family molecules in the tumour microenvironment. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2008;8:467–477. A good review of the basic biology of the expanding B7 family of regulatory molecules in the context of cancer immunology.
-
-
- Mellor AL, Keskin DB, Johnson T, Chandler P, Munn DH. Cells expressing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibit T cell responses. J. Immunol. 2002;168:3771–3776. - PubMed
-
- Friberg M, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase contributes to tumor cell evasion of T cell-mediated rejection. J. Cancer. 2002;101:151–155. - PubMed
-
- Hou DY, et al. Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in dendritic cells by stereoisomers of 1-methyl-tryptophan correlates with antitumor responses. Cancer Res. 2007;67:792–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

